Overview
Digital healthcare fundamentally differs from traditional healthcare in its reliance on technology for service delivery. It emphasizes remote access and real-time data sharing, contrasting sharply with traditional healthcare, which focuses on in-person consultations and established medical practices. This distinction is crucial: digital healthcare enhances accessibility and convenience, making it a compelling choice for many. However, traditional healthcare excels in providing comprehensive care and fostering trust through personal interactions. Understanding these differences is essential for navigating the evolving landscape of healthcare options.
Introduction
Digital healthcare is fundamentally reshaping the medical landscape, ushering in innovative technologies that significantly enhance accessibility and efficiency in patient care.
As telemedicine and mobile health applications gain increasing traction, it is crucial to understand the core differences between this modern approach and traditional healthcare.
However, the convenience of digital solutions presents the challenge of ensuring comprehensive care, particularly in situations that necessitate personal interaction.
How do these two models coexist? What factors should patients consider when navigating their healthcare options? These questions are vital as we explore the future of healthcare.
Define Digital Healthcare and Traditional Healthcare
Digital healthcare signifies a transformative approach to healthcare, leveraging digital technologies such as telemedicine, mobile health applications, and electronic health records to enhance the delivery and management of medical services. This innovative paradigm emphasizes , real-time data sharing, and active user engagement through technology.
In stark contrast, conventional medical services rely on face-to-face consultations, physical assessments, and long-established medical practices that have stood the test of time. This traditional model often necessitates in-person interactions between patients and healthcare providers, adhering to established protocols and procedures without the integration of electronic tools.
The shift towards digital healthcare not only represents a cultural evolution in care provision but also prioritizes accessibility and efficiency. Meanwhile, conventional medicine continues to underscore the importance of personal interaction and time-honored methods.
Embracing digital healthcare is not merely an option; it is a necessary step forward in modern healthcare.
Compare Effectiveness: Digital vs. Traditional Healthcare
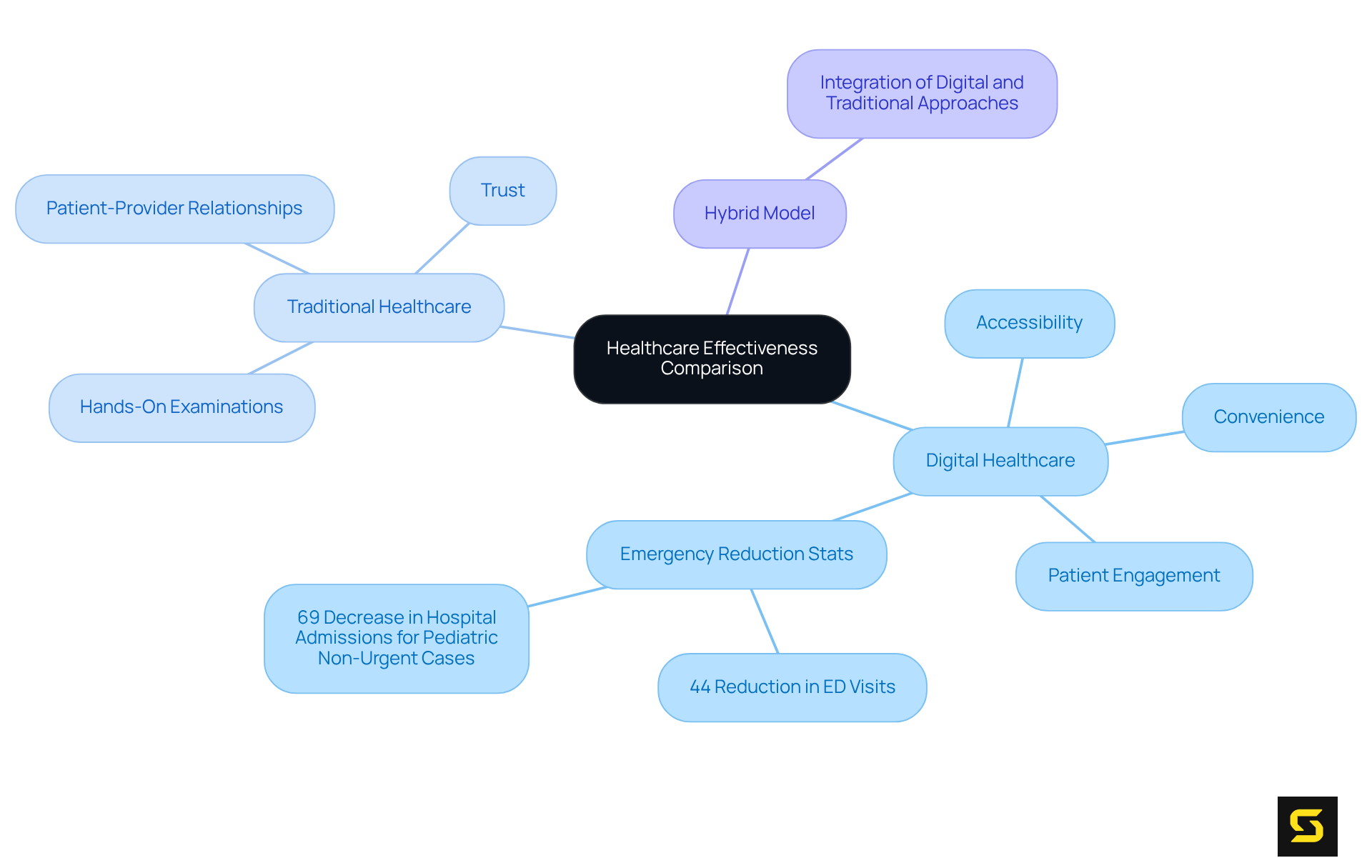
Digital healthcare consistently showcases significant advantages in accessibility and convenience, particularly through telemedicine, which effectively reduces wait times and enables individuals to consult specialists regardless of their location. Research reveals that digital healthcare services can significantly enhance patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans, with telemedicine resulting in a remarkable 44% reduction in emergency department visits and a 69% decrease in hospital admissions for pediatric non-urgent cases, as demonstrated by the virtualKIDS service. This seamless access to information and medical providers encourages a proactive approach to health management.
Nevertheless, traditional healthcare maintains its strengths in situations that require hands-on examinations or procedures, where the physical presence of a healthcare provider is indispensable. Face-to-face interactions often cultivate deeper patient-provider relationships, enhancing trust and communication, which are vital for effective treatment. As E.H. notes, "the quality of telehealth-delivered palliative support and medical services is quite strong," yet ongoing discussions persist regarding the overall effectiveness of telehealth in comparison to in-person visits.
While provide innovative solutions that enhance efficiency and access, conventional medicine remains essential for comprehensive assessments and interventions. The integration of both approaches can establish a hybrid model that optimizes patient outcomes, ensuring individuals receive the highest quality care tailored to their unique needs.
Evaluate Pros and Cons of Each Healthcare Model
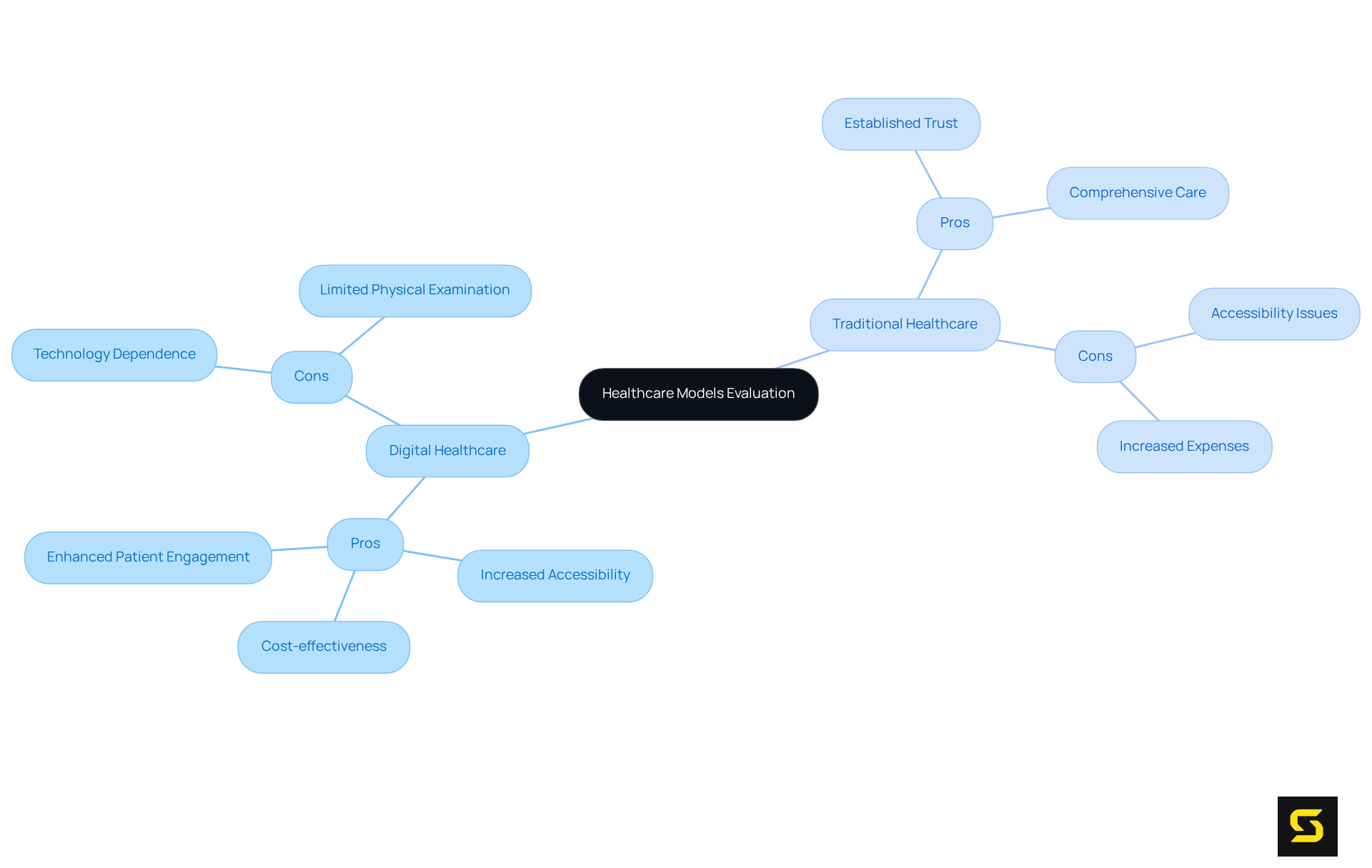
The landscape of medical services is transformed by the multitude of . Increased Accessibility stands out as a key benefit; patients can access healthcare services from virtually any location, effectively dismantling barriers related to distance and mobility. This is particularly crucial for individuals residing in isolated or underserved regions, where traditional medical facilities may be sparse. Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of digital healthcare is a significant advantage. Digital solutions can dramatically reduce operational expenses for medical providers while simultaneously lowering costs for individuals, such as the travel expenses associated with in-person visits. For instance, telehealth services have demonstrated a capacity to decrease hospital admissions by facilitating earlier identification of health issues, ultimately resulting in substantial cost savings. Additionally, enhanced patient engagement is fostered through digital healthcare tools that empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare, leading to improved health outcomes. Personal health apps, for example, enable users to effectively track vital signs and manage their medical information.
Nevertheless, the field of digital healthcare faces its own set of challenges. Technology Dependence poses a significant hurdle; patients lacking access to necessary technology or possessing limited digital literacy may face obstacles in utilizing these services. This reliance on digital healthcare can create a technological divide, leaving some individuals with insufficient medical options. Moreover, the Limited Physical Examination presents a drawback, as certain medical conditions require in-person assessments that digital services cannot provide. Imaging tests and blood work, for instance, necessitate physical presence, underscoring the limitations of remote consultations.
Conversely, traditional healthcare presents its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Established Trust is a hallmark of long-standing relationships between patients and providers, enhancing communication and fostering a more personalized care experience. Additionally, Comprehensive Care is facilitated through in-person visits, which allow for thorough examinations and immediate interventions—crucial for diagnosing complex health issues.
However, traditional healthcare also has notable downsides. Accessibility Issues can arise, as patients may encounter challenges related to travel and wait times, hindering timely access to care. Furthermore, Increased Expenses are often associated with conventional medical services, as overhead charges linked to physical locations and personnel can render these services less accessible for certain individuals. In conclusion, both digital healthcare and traditional healthcare modalities present unique advantages and challenges that warrant careful consideration.
Assess Suitability for Patient Needs and Scenarios
The decision between digital and conventional medical services hinges on the specific needs of the individual and the context of care. Consider the following scenarios:
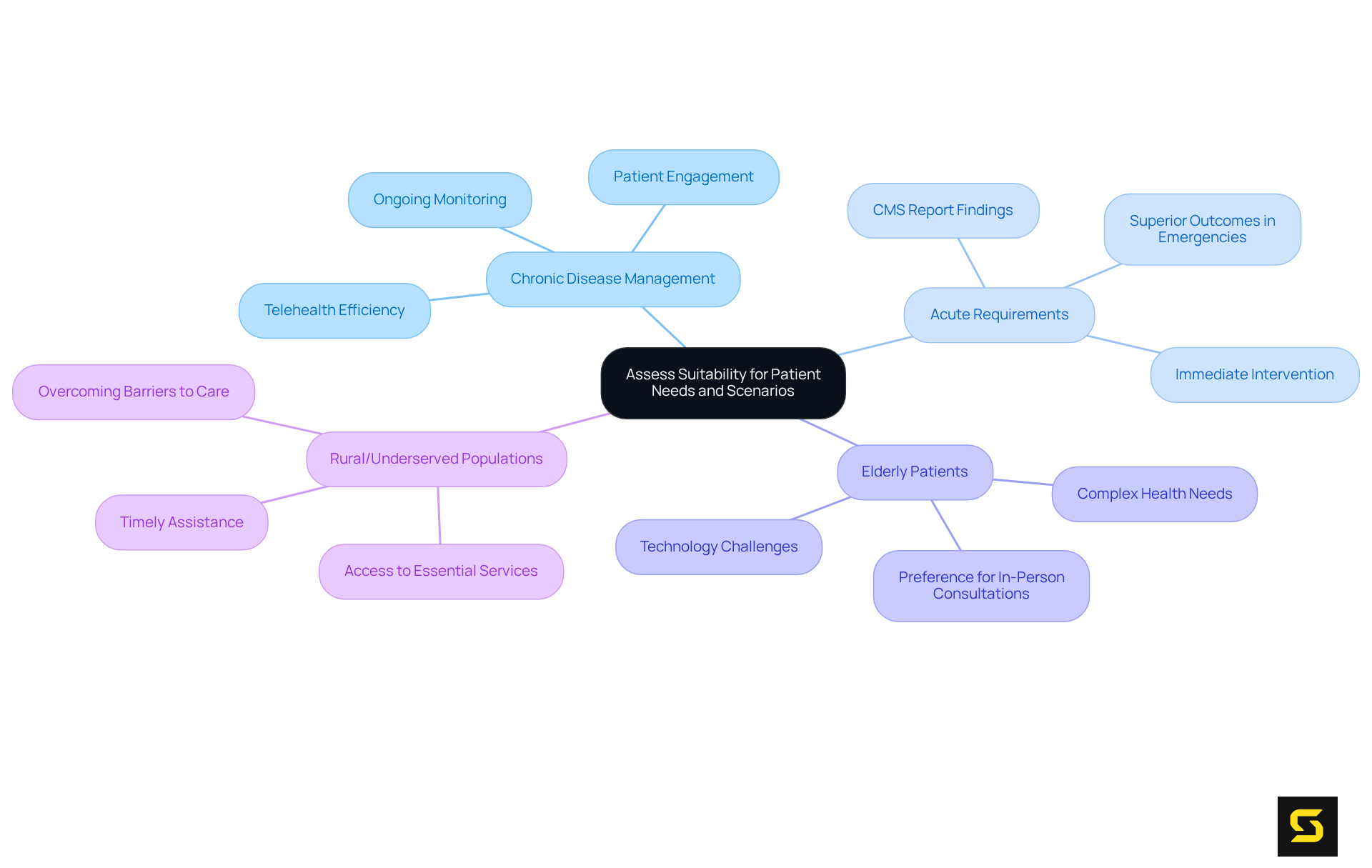
- Chronic Disease Management: Digital healthcare stands out in the management of chronic conditions, where ongoing monitoring and patient engagement are crucial. Patients can leverage applications to track symptoms and maintain consistent communication with healthcare providers, significantly enhancing their capacity to manage their conditions effectively.
- Acute Requirements: Conventional medical services are typically more appropriate for urgent situations, such as emergencies or cases requiring immediate physical assessment and intervention. Research indicates that traditional settings often yield superior outcomes for acute conditions, facilitating rapid response and thorough evaluation. Notably, a CMS report highlights that the mortality rate for Acute Hospital Treatment at Home inpatients was lower across all top 25 MS-DRGs, underscoring the effectiveness of conventional treatment in acute scenarios.
Digital healthcare services serve as a vital link for patients in rural and underserved populations, providing access to essential services that may not be locally available. This approach can significantly improve health outcomes by ensuring timely assistance for individuals who might otherwise face barriers to care.
- Elderly Patients: While some older adults may appreciate digital services, many prefer traditional methods due to their comfort with face-to-face interactions and potential challenges with technology. The preference for in-person consultations can be particularly pronounced among older individuals, who often have complex health needs that necessitate careful attention.
The Acute Hospital Assistance at Home initiative, supported by the AMA, has shown promising results, emphasizing the importance of conventional medical effectiveness in acute treatment settings. Ultimately, the decision between digital and traditional healthcare should be informed by , preferences, and the specific healthcare context. Balancing these elements is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes and ensuring effective care delivery.
Conclusion
The exploration of digital healthcare versus traditional healthcare reveals a fundamental shift in the delivery and accessibility of medical services. This comparative analysis underscores the necessity of integrating digital solutions into healthcare practices to enhance accessibility and efficiency, while also recognizing the enduring value of traditional methods that prioritize personal interaction and comprehensive care.
Key arguments highlight the advantages of digital healthcare, including:
- Increased accessibility
- Cost-effectiveness
- Improved patient engagement through technology
Conversely, traditional healthcare excels in scenarios requiring:
- Hands-on examinations
- Fostering strong patient-provider relationships
This discussion emphasizes that both models possess unique strengths and weaknesses, suggesting that a hybrid approach could optimize patient outcomes by combining the best of both worlds.
Ultimately, the decision between digital and traditional healthcare should be tailored to individual needs and specific healthcare contexts. By understanding the nuances of each model, patients can make informed choices that align with their health requirements, ensuring they receive the most appropriate care. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, embracing a balanced approach that leverages both digital innovations and traditional practices will be essential for delivering high-quality, patient-centered care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is digital healthcare?
Digital healthcare is a transformative approach to healthcare that utilizes digital technologies like telemedicine, mobile health applications, and electronic health records to improve the delivery and management of medical services.
How does digital healthcare differ from traditional healthcare?
Digital healthcare emphasizes remote access, real-time data sharing, and active user engagement through technology, while traditional healthcare relies on face-to-face consultations, physical assessments, and established medical practices that require in-person interactions.
What are the advantages of digital healthcare?
Digital healthcare prioritizes accessibility and efficiency, allowing for enhanced patient engagement and streamlined medical services compared to conventional methods.
Why is embracing digital healthcare important?
Embracing digital healthcare is essential for modern healthcare as it represents a necessary evolution in care provision to meet the demands of today's patients and healthcare environment.
What does traditional healthcare emphasize?
Traditional healthcare emphasizes the importance of personal interaction between patients and healthcare providers, relying on time-honored methods and established protocols without the integration of electronic tools.





