Overview
Ensuring your SaaS product achieves HIPAA compliance is not merely a suggestion; it is a necessity. Key steps include:
- Conducting a thorough risk assessment
- Establishing robust administrative and technical safeguards
- Formulating comprehensive business associate agreements
This article delineates these critical steps and underscores the vital role of continuous monitoring and staff training in maintaining compliance. Such measures significantly mitigate the risk of data breaches and cultivate trust with users, reinforcing the importance of proactive compliance strategies.
Introduction
Navigating the complex landscape of healthcare regulations is essential for Software as a Service (SaaS) providers who are committed to protecting sensitive patient information. Understanding the intricacies of HIPAA compliance transcends mere legal obligation; it is a vital step towards establishing trust with users and safeguarding their data.
In an era marked by evolving regulations and escalating cyber threats, how can SaaS companies effectively ensure their products meet these stringent requirements? By exploring the key steps to achieve HIPAA compliance, organizations can uncover both the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in their pursuit of the highest standards of health information security.
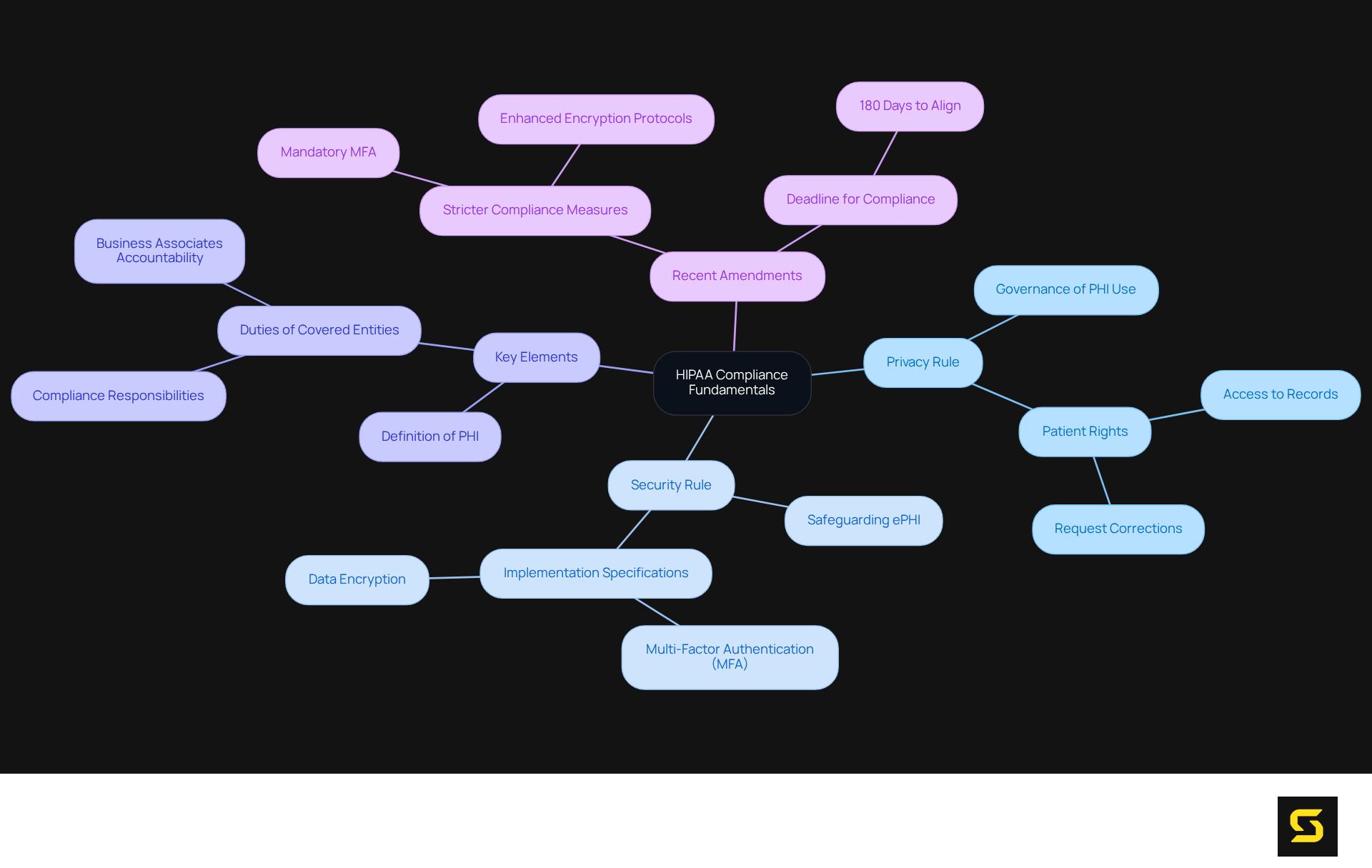
Understand HIPAA Compliance Fundamentals
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) stands as a pivotal federal law designed to protect sensitive patient health information from unauthorized disclosure. For Software as a Service (SaaS) providers, comprehending healthcare privacy regulations is essential to ensure they are HIPAA compliant. This includes critical components such as the Privacy Rule and the Security Rule. The Privacy Rule governs the use and disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI), while the Security Rule sets forth standards for safeguarding electronic PHI (ePHI).
To ensure compliance and avert substantial penalties, SaaS providers must understand several key elements:
- Definition of PHI: It is crucial to recognize what constitutes PHI, which encompasses any health information that can identify an individual.
- Patient Rights: Patients possess specific rights regarding their information, including the right to access and request corrections to their health records.
- Duties of Covered Entities and Business Associates: Both parties are required to adhere to privacy regulations, with business associates being directly accountable for being HIPAA compliant since the 2013 Omnibus Rule.
Recent amendments to privacy regulations, effective in 2025, underscore the necessity for stricter compliance measures, including mandatory multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enhanced information encryption protocols. Organizations will have 180 days to align with these new standards, underscoring the urgency for SaaS providers to adjust their systems accordingly.
Practical examples underscore the critical importance of adhering to health information regulations in software development. For instance, healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting robust security measures to protect ePHI, as evidenced by a dramatic increase in data breaches—impermissibly disclosed records surged from 51.9 million to 168 million between 2022 and 2023.
By prioritizing HIPAA compliant measures in health data protection regulations, SaaS providers not only mitigate the risk of significant penalties but also cultivate trust with their users, ensuring that sensitive health information remains secure and private.
Implement Key HIPAA Compliance Steps for SaaS Products
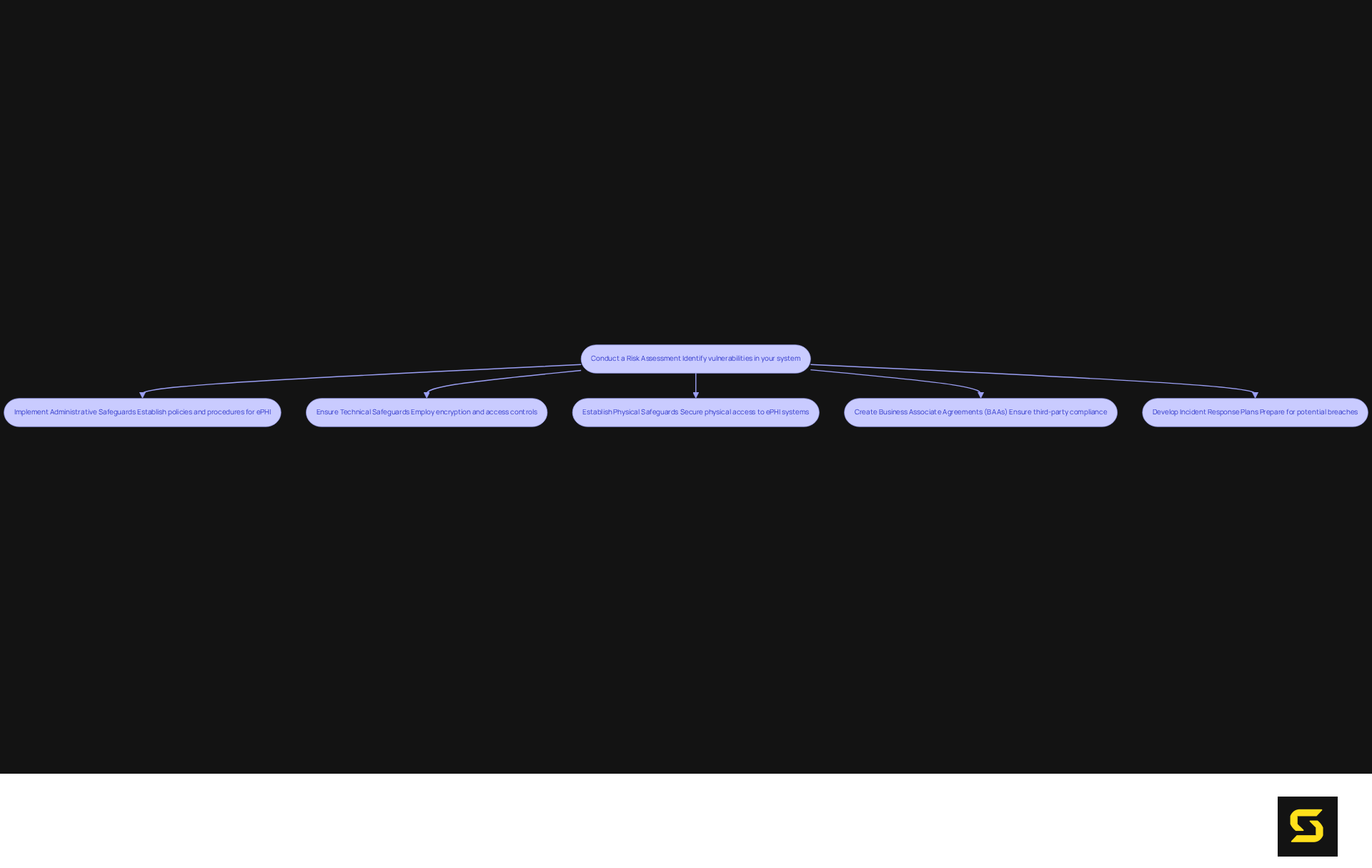
To ensure your SaaS product is HIPAA compliant, it is imperative to follow these key steps:
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Begin by identifying potential vulnerabilities in your system that could expose protected health information (PHI). This assessment must be comprehensive, encompassing both technical and administrative safeguards. Regular audits and evaluations are essential; a staggering 70% of organizations reported experiencing an incident in the past 12 months. This statistic underscores the necessity for vigilance and ongoing training programs.
- Implement Administrative Safeguards: Establish robust policies and procedures to effectively manage the selection, development, implementation, and maintenance of protective measures for electronic PHI (ePHI). This includes appointing a dedicated HIPAA compliance officer, especially considering that only 34% of healthcare organizations have fully documented their compliance efforts. Training programs should cover essential topics such as password protection and information handling, aiming to , which account for 43% of healthcare information breaches.
- Ensure Technical Safeguards: Employ encryption, secure user authentication, and access controls to protect ePHI. It is crucial to consistently refresh software to address vulnerabilities, as technical failures are responsible for 21% of healthcare information breaches. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) can significantly enhance protection.
- Establish Physical Safeguards: Safeguard physical access to systems that store ePHI. This includes securing facilities and ensuring that devices are not left unattended. Physical safeguards are vital in preventing unauthorized access.
- Create Business Associate Agreements (BAAs): If your SaaS product interacts with third-party vendors handling PHI, it is essential to have BAAs in place. These agreements delineate the responsibilities of vendors to ensure they are HIPAA compliant, which is critical for ensuring security across all platforms.
- Develop Incident Response Plans: Prepare for potential breaches by having a comprehensive response strategy that includes notification procedures and remediation steps. Given that the average cost of a healthcare data breach exceeds $7.13 million, a proactive approach can significantly mitigate financial and reputational damage.
Establish Continuous Monitoring and Staff Training Programs
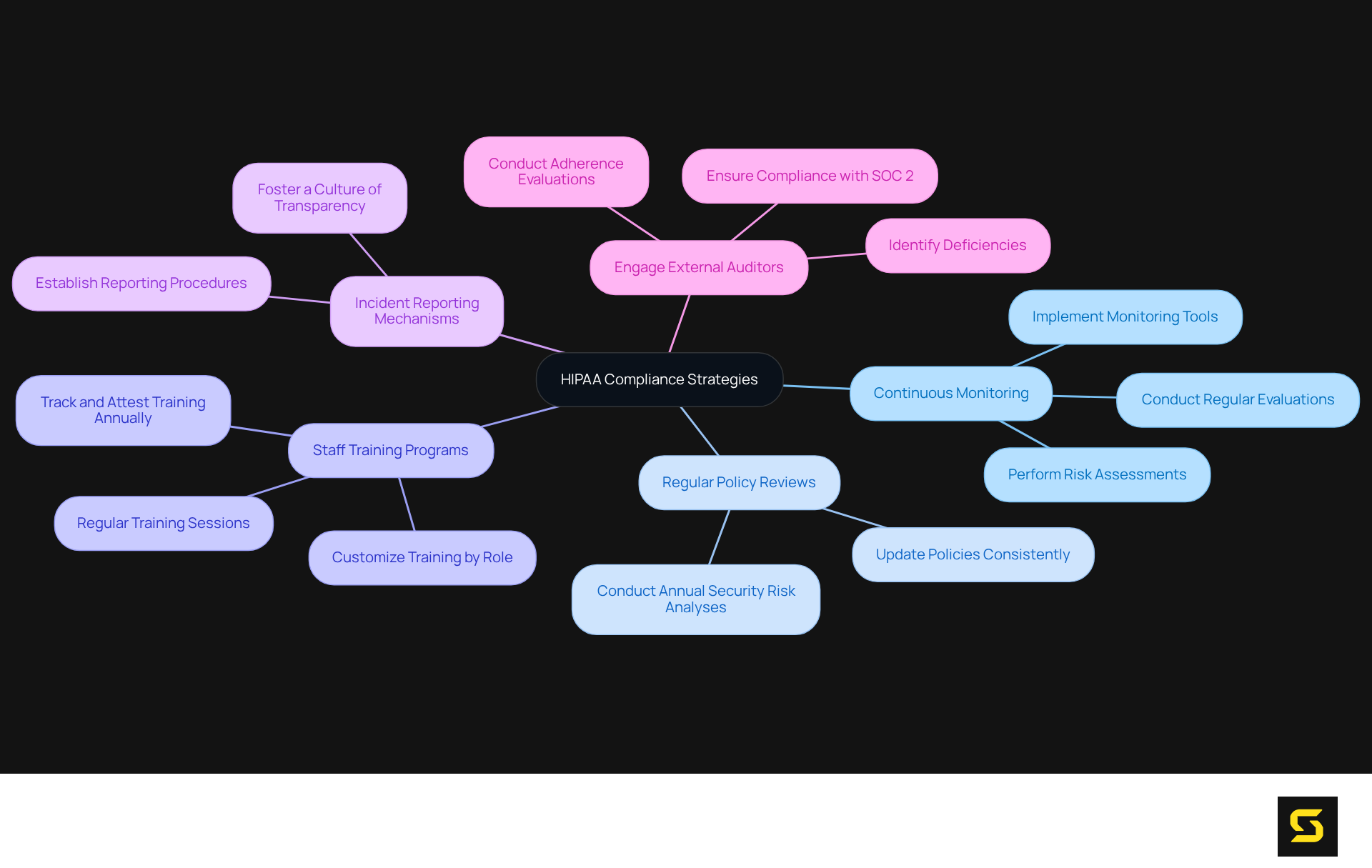
To ensure they are , organizations must prioritize continuous monitoring and robust staff training programs.
- Continuous Monitoring: Organizations must implement tools and processes that support ongoing adherence to HIPAA regulations. This requires conducting regular evaluations of protective measures and performing risk assessments to identify and address new vulnerabilities. Given that healthcare organizations are prime targets for cyberattacks, often due to insufficient protective practices, continuous vigilance is essential.
- Regular Policy Reviews: It is imperative that policies and procedures are consistently updated to reflect changes in regulations and organizational practices. This proactive approach aligns compliance efforts with current standards, thereby mitigating the risk of noncompliance and potential fines. Conducting annual security risk analyses is crucial for uncovering weaknesses in data security practices.
- Staff Training Programs: Regular training sessions for all employees regarding HIPAA regulations and the importance of safeguarding patient health information (PHI) are vital. Customizing training to fit specific roles increases its relevance and effectiveness, ensuring that employees fully understand their responsibilities in upholding these regulations. It is essential that annual training is tracked and attested to, as human error remains a leading cause of data breaches.
- Incident Reporting Mechanisms: Establishing clear procedures for reporting potential breaches or regulatory issues is critical. Fostering a culture of transparency encourages employees to report concerns without fear of repercussions, which is vital for early detection and response to security threats.
- Engage External Auditors: Employing outside auditors for adherence evaluations provides an impartial assessment of compliance status. Their insights can help identify deficiencies in existing practices and suggest necessary enhancements. This ensures a thorough approach to compliance, including readiness evaluations to align with relevant regulations and SOC 2 requirements.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can become HIPAA compliant and significantly enhance their overall security posture, thereby fostering trust among patients and stakeholders.
Conclusion
Ensuring HIPAA compliance for SaaS products transcends mere regulatory obligation; it embodies a crucial commitment to safeguarding sensitive patient information. By thoroughly grasping the fundamentals of HIPAA, including the Privacy and Security Rules, SaaS providers can forge a robust framework that protects electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) from unauthorized access and breaches.
Key steps—such as conducting risk assessments, implementing administrative and technical safeguards, and fostering continuous monitoring and staff training—are essential components of a comprehensive compliance strategy. These measures not only mitigate the risk of financial penalties and data breaches but also cultivate trust with users who depend on the security of their health information. The urgency for compliance intensifies with impending regulatory changes, making it imperative for organizations to act swiftly.
The significance of HIPAA compliance extends beyond legal adherence; it reflects a steadfast commitment to ethical standards in healthcare technology. By prioritizing the protection of patient data, SaaS providers fulfill their responsibilities and contribute to a more secure healthcare environment. Embracing these best practices is vital for any organization aiming to thrive in the healthcare sector while upholding the highest standards of data protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is HIPAA and why is it important for SaaS providers?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a federal law designed to protect sensitive patient health information from unauthorized disclosure. For SaaS providers, understanding HIPAA is essential to ensure compliance with healthcare privacy regulations.
What are the key components of HIPAA?
The key components of HIPAA include the Privacy Rule, which governs the use and disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI), and the Security Rule, which sets standards for safeguarding electronic PHI (ePHI).
What constitutes Protected Health Information (PHI)?
Protected Health Information (PHI) includes any health information that can identify an individual.
What rights do patients have regarding their health information under HIPAA?
Patients have specific rights, including the right to access their health records and request corrections to them.
What are the responsibilities of Covered Entities and Business Associates under HIPAA?
Both Covered Entities and Business Associates must adhere to privacy regulations. Since the 2013 Omnibus Rule, Business Associates have been directly accountable for being HIPAA compliant.
What are the upcoming changes to HIPAA regulations effective in 2025?
The upcoming changes include stricter compliance measures such as mandatory multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enhanced information encryption protocols. Organizations will have 180 days to comply with these new standards.
Why is it critical for SaaS providers to prioritize HIPAA compliance?
Prioritizing HIPAA compliance helps SaaS providers mitigate the risk of significant penalties and build trust with their users by ensuring that sensitive health information remains secure and private.
What recent trends highlight the importance of HIPAA compliance in software development?
There has been a dramatic increase in data breaches, with impermissibly disclosed records rising from 51.9 million to 168 million between 2022 and 2023, underscoring the need for robust security measures to protect ePHI.





