Overview
SaaS, or Software as a Service, represents a transformative cloud-based software delivery model that empowers users to access applications via the internet without the need for local installations, typically through a subscription-based pricing structure. This model not only enhances operational flexibility but also significantly reduces hardware costs.
Evolving from early time-sharing systems, SaaS has emerged as a dominant software solution, profoundly impacting business efficiency and driving innovation across various industries. To leverage these advantages, organizations must consider integrating SaaS into their operational framework.
Introduction
Understanding the landscape of modern software delivery reveals a transformative trend that has fundamentally reshaped business operations: Software as a Service (SaaS). This innovative model empowers users to access applications via the internet, significantly diminishing the need for local installations and extensive hardware setups.
As organizations increasingly embrace SaaS solutions for their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility, a critical question emerges: what does SaaS truly represent, and how has it evolved into a cornerstone of contemporary business operations?
Delving into this topic not only clarifies the definition of SaaS but also elucidates its substantial impact on efficiency, collaboration, and the future trajectory of technology.
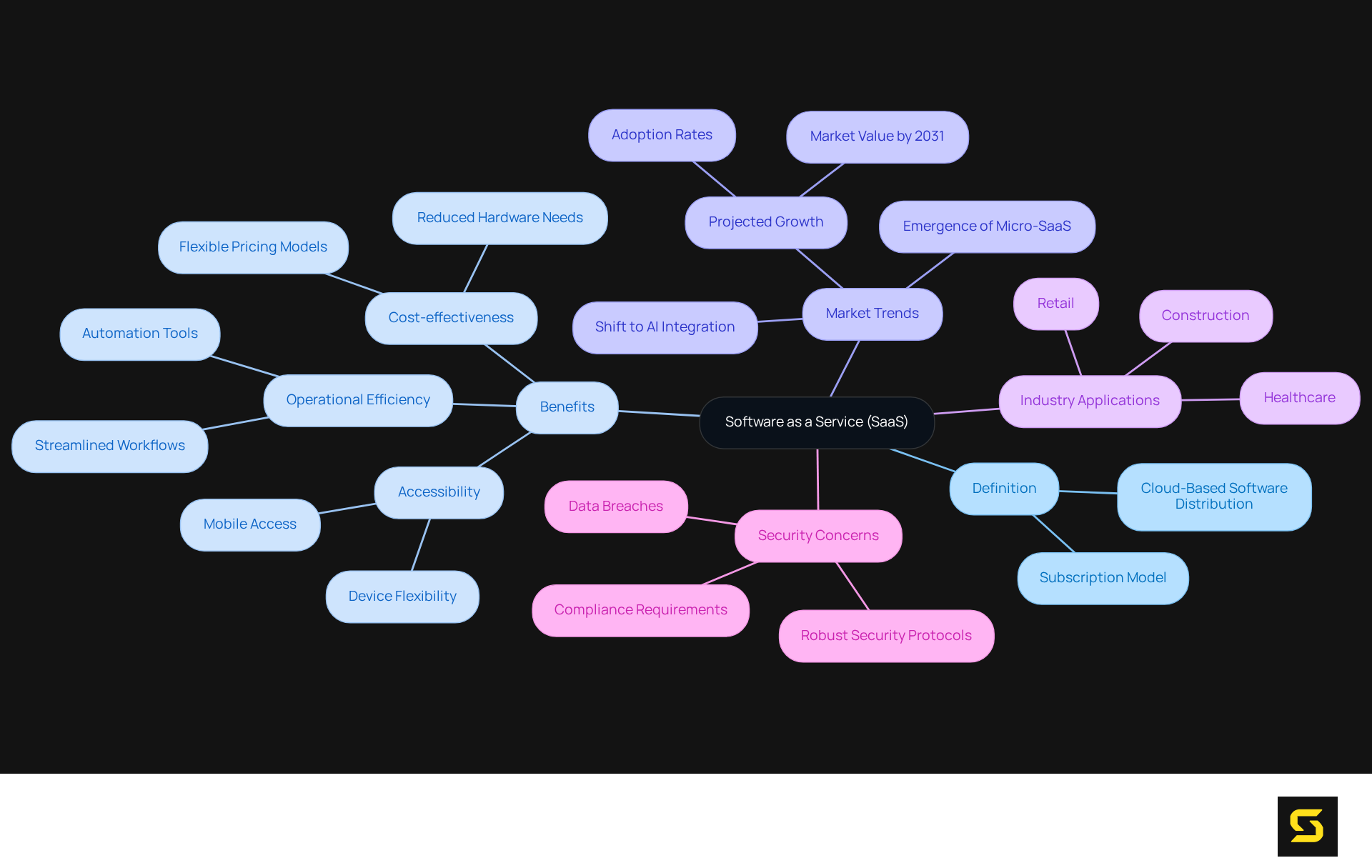
Define SaaS: Understanding Software as a Service
When discussing cloud-based software distribution, many people wonder what does SaaS stand for, as it epitomizes a revolutionary method that empowers users to access applications via the internet, eliminating the need for local installations. In this paradigm, software is hosted on the provider's servers, allowing organizations to pay a subscription fee for usage. This model significantly reduces the demand for extensive hardware and software setups, facilitating swift adoption and scalability of solutions. By 2025, approximately 85% of businesses are projected to leverage software-as-a-service solutions, leading to a growing interest in what does SaaS stand for, which underscores its increasing dominance in the market.
SaaS applications are designed for accessibility, permitting users to connect from any device with internet access, thereby enhancing operational flexibility and convenience. Industry leaders underscore the significance of this accessibility; for example, Steve Jobs asserted that a seamless mobile experience amplifies engagement and productivity. Furthermore, the software-as-a-service landscape is transitioning towards flexible, pay-as-you-go models, moving away from traditional flat subscriptions.
The shift to software as a service, which is what does SaaS stand for, is evident across various industries, including healthcare and retail, that adopt these solutions to boost operational efficiency and optimize workflows. Notable examples of organizations effectively utilizing software-as-a-service include Gojek and Paystack, which have innovated in eCommerce and fintech by leveraging these platforms to enhance their service offerings. This model not only improves operational efficiency but also aligns with the evolving needs of businesses seeking agile and cost-effective solutions. Moreover, as security concerns escalate, implementing robust security protocols in cloud-based solutions has become essential for maintaining customer trust and ensuring compliance with regulations.
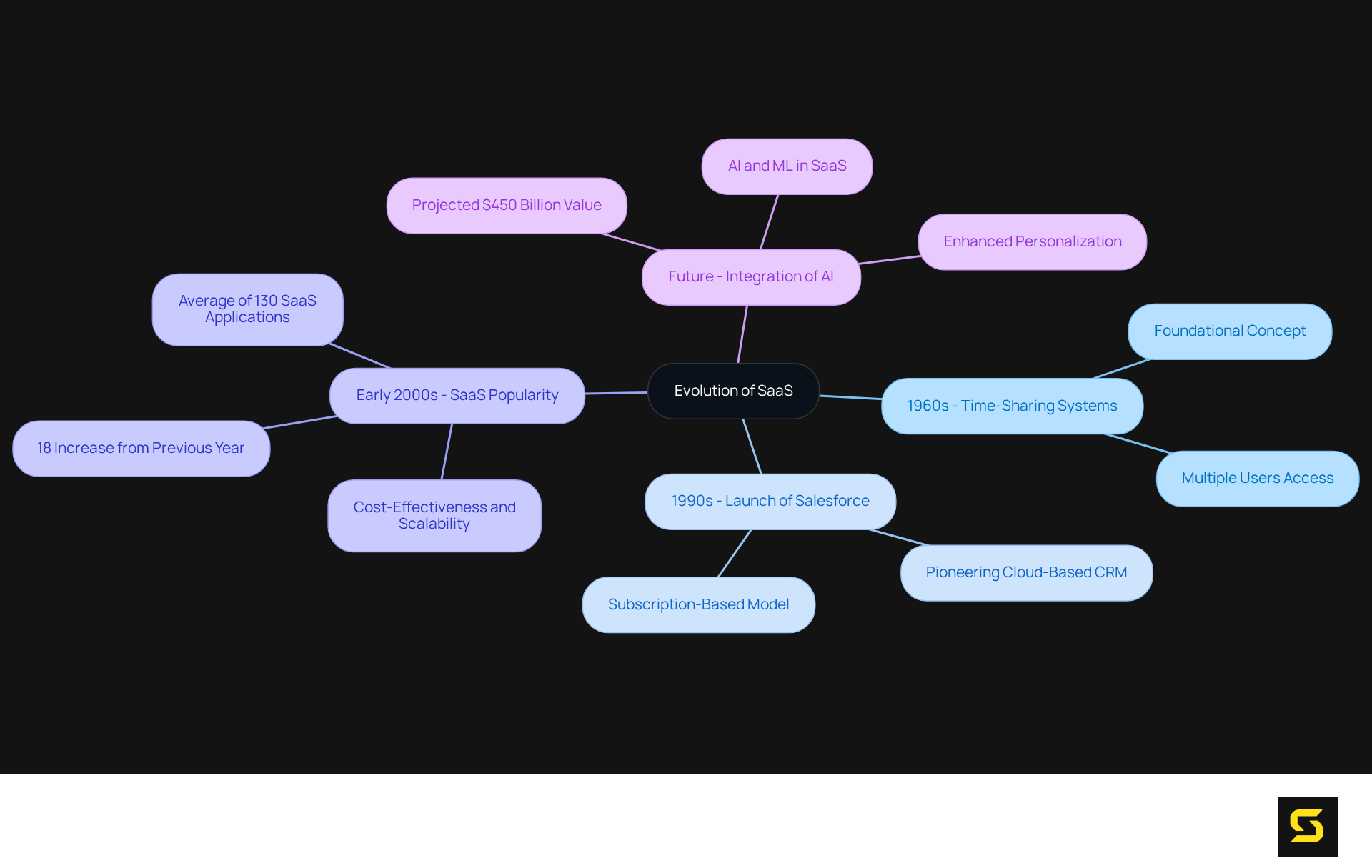
Trace the Evolution of SaaS: Historical Context and Development
The origins of Software as a Service (SaaS) can be traced back to the 1960s, when time-sharing systems allowed multiple users to access a single mainframe computer. This foundational concept laid the groundwork for understanding what does SaaS stand for and how it would evolve into modern SaaS.
A pivotal shift occurred in the late 1990s with the advent of the internet, culminating in the launch of Salesforce in 1999. This groundbreaking innovation pioneered cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM), transforming the delivery and consumption of software. Salesforce recognized the limitations of the traditional one-time license model and instead introduced a monthly subscription-based approach, which leads to the question, what does SaaS stand for in the CRM sector?
As broadband technology and cloud computing infrastructure advanced, SaaS gained momentum, emerging as the preferred software delivery model by the early 2000s. Today, organizations utilize an average of 130 SaaS applications, reflecting an 18% increase from the previous year, underscoring the importance and prevalence of these solutions in operational activities.
To understand what does SaaS stand for, it's important to note that it encompasses a diverse array of applications, ranging from productivity tools to enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, showcasing its adaptability to various business needs. The continuous evolution of SaaS is recognized for its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and support for remote work, aligning with changing consumer expectations for accessibility and efficiency in software solutions.
Furthermore, the integration of AI agents is anticipated to yield $450 billion in value, highlighting the future potential of software as it continues to evolve.
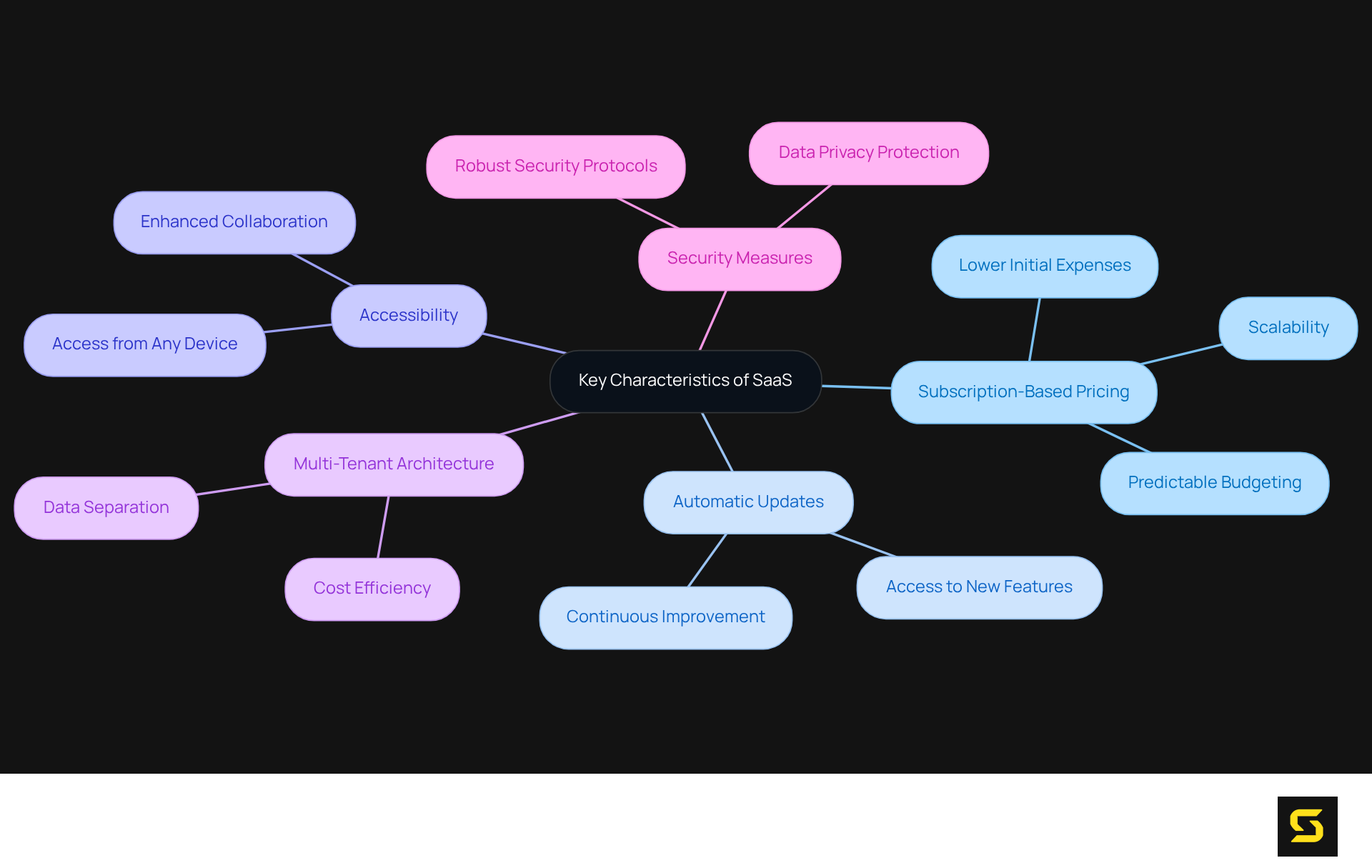
Identify Key Characteristics of SaaS: Features and Benefits
To understand what does SaaS stand for, one should note that its key characteristics include subscription-based pricing, automatic updates, and accessibility from any internet-connected device. To understand what does SaaS stand for, it's important to note that SaaS applications typically operate on a multi-tenant architecture, enabling various users to utilize the same infrastructure while keeping their data separate. This model significantly reduces costs for both providers and users by eliminating the need for extensive hardware investments and ongoing maintenance. In fact, the average software-as-a-service expenditure per employee has surged to $4,830, marking a 21.9% increase year over year and underscoring the financial implications of adopting these services.
Subscription-based pricing offers numerous advantages, including predictable budgeting and lower initial expenses, which facilitate easier financial management for companies. Moreover, SaaS solutions provide scalability, allowing organizations to adjust their subscription levels according to evolving requirements. This flexibility is essential as businesses expand or pivot, enabling them to optimize their software usage without incurring unnecessary costs.
Enhanced collaboration stands out as another significant benefit, as users can access the same application simultaneously from various locations, fostering teamwork and communication. Additionally, SaaS providers typically invest in robust security measures to protect user information, addressing the growing concerns surrounding data privacy and protection. In today's digital landscape, organizations that adopt SaaS solutions often report improved operational efficiency and reduced risks related to data breaches, leading to a common inquiry: what does SaaS stand for?
Industry leaders assert that the subscription model not only drives innovation but also promotes continuous improvement. Swetha GP, VP of Delivery, notes that despite potential challenges such as data privacy concerns and heightened competition, the SaaS market remains resilient and poised for success. This dynamic creates a win-win scenario where users benefit from regular updates and new features, while providers secure a consistent revenue stream. Furthermore, 33% of organizations have consolidated unnecessary applications and accounts, illustrating the growing importance of efficient software management in resource optimization. The global SaaS market is projected to exceed $200 billion by 2025, emphasizing the necessity of understanding service frameworks in the current market environment.
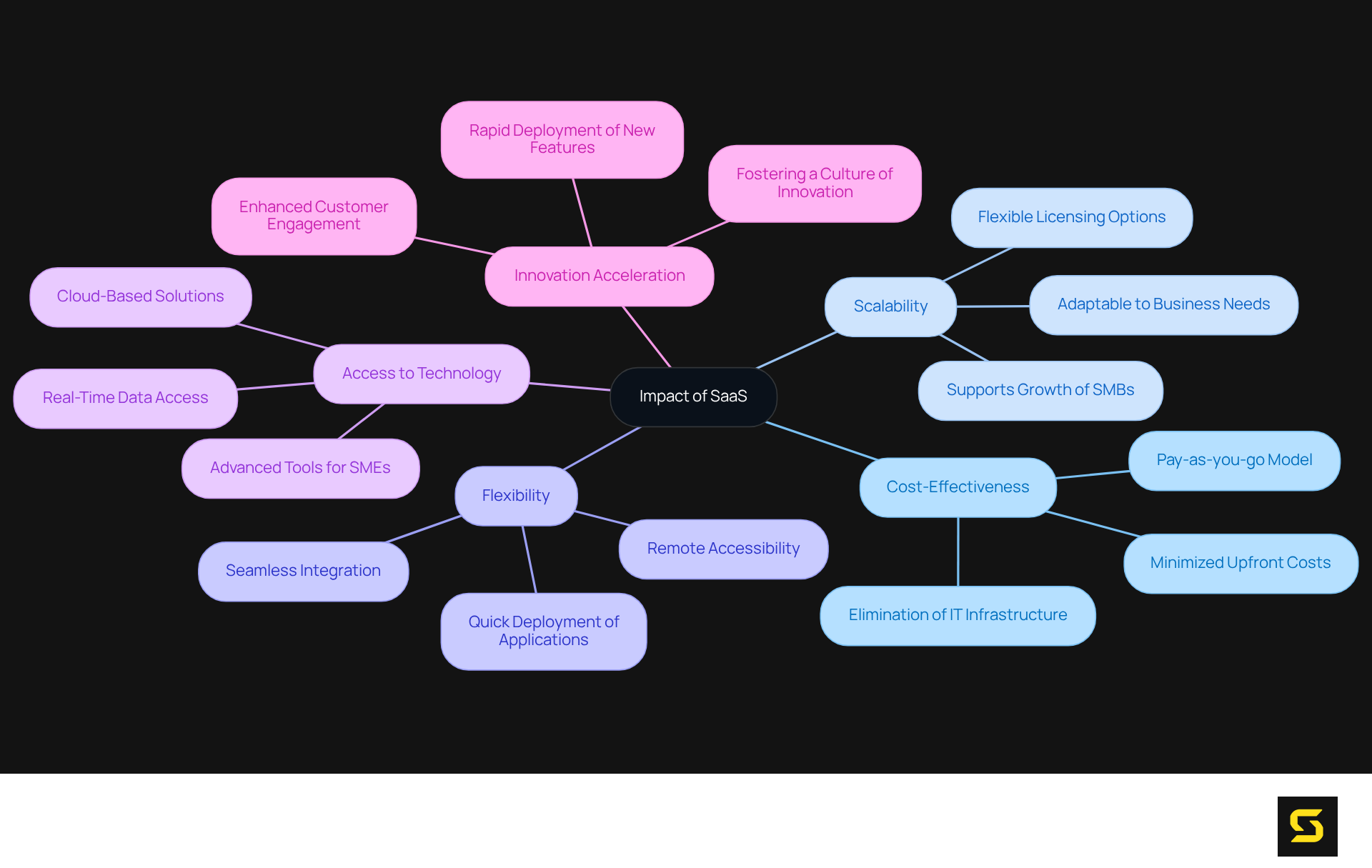
Highlight the Importance of SaaS: Impact on Business and Technology
In discussing what does SaaS stand for, it's clear that it has fundamentally transformed organizational operations by delivering cost-effective, scalable, and flexible software solutions. This innovative model has democratized access to advanced technologies, empowering small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to leverage tools that were once the domain of larger corporations. The subscription-based approach minimizes upfront costs, allowing businesses to allocate their resources more strategically.
Furthermore, understanding what does SaaS stand for accelerates innovation by enabling the rapid deployment of new applications and features, facilitating swift responses to customer feedback and market dynamics. Organizations that utilize cloud-based software experience enhanced operational efficiency, improved customer engagement, and a significant competitive advantage in their respective industries.
For instance, companies employing software-as-a-service solutions, leading to an understanding of what does SaaS stand for, have reported substantial cost reductions, with many eliminating the need for extensive IT infrastructure and significantly shortening time-to-market for new products.
According to Sandeep Kumar, Sr. VP & Head Global Consulting, 'SMBs are scaling. They are agile and respond to market needs faster than big-brand competition can.' This agility not only fosters a culture of innovation but also positions companies to adapt quickly to evolving market conditions, ultimately driving growth and success.
Additionally, SaaS applications offer seamless integration capabilities, enabling organizations to connect various tools and systems without significant disruption.
Conclusion
Software as a Service (SaaS) signifies a transformative approach to software delivery, empowering users to access applications via the internet without the encumbrances of local installations. This model streamlines access and reduces hardware costs, fostering a flexible environment for businesses to scale their operations efficiently. As the SaaS landscape continues to evolve, its significance in modern business practices becomes increasingly pronounced.
This article delineates the historical development of SaaS, tracing its roots from the 1960s to its current prominence, marked by innovations such as Salesforce. Key characteristics—subscription-based pricing, automatic updates, and multi-tenant architecture—are essential features that contribute to its widespread adoption. The benefits of SaaS, including enhanced collaboration, cost-effectiveness, and robust security measures, further underscore its value in today’s digital landscape.
Ultimately, the evolution of SaaS transcends mere technological advancement; it represents a paradigm shift in how businesses operate and innovate. Embracing this model allows organizations, regardless of size, to leverage cutting-edge tools that enhance operational efficiency and customer engagement. As the SaaS market continues to grow, understanding its implications will be crucial for businesses aiming to thrive in an increasingly competitive environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does SaaS stand for?
SaaS stands for Software as a Service, which is a cloud-based software distribution model that allows users to access applications via the internet.
How does the SaaS model work?
In the SaaS model, software is hosted on the provider's servers, and organizations pay a subscription fee for usage, eliminating the need for local installations.
What are the benefits of using SaaS?
SaaS significantly reduces the demand for extensive hardware and software setups, facilitates swift adoption and scalability of solutions, and enhances operational flexibility by allowing access from any device with internet access.
What is the projected trend for SaaS adoption by 2025?
By 2025, approximately 85% of businesses are projected to leverage software-as-a-service solutions, indicating its growing dominance in the market.
How is the SaaS landscape evolving?
The SaaS landscape is transitioning towards flexible, pay-as-you-go models, moving away from traditional flat subscription fees.
Which industries are adopting SaaS solutions?
Various industries, including healthcare and retail, are adopting SaaS solutions to boost operational efficiency and optimize workflows.
Can you provide examples of organizations using SaaS?
Notable examples of organizations effectively utilizing SaaS include Gojek and Paystack, which have innovated in eCommerce and fintech by leveraging these platforms.
What role does security play in SaaS?
As security concerns escalate, implementing robust security protocols in cloud-based solutions has become essential for maintaining customer trust and ensuring compliance with regulations.





