Overview
The article asserts the essential features that medical software must possess to effectively support healthcare providers. It highlights that crucial functionalities—including interoperability, user-friendly interfaces, data security, real-time analytics, EHR integration, telemedicine capabilities, customizable workflows, regulatory compliance, and patient engagement tools—are vital for enhancing operational efficiency and improving patient care outcomes. By incorporating these elements, healthcare providers can ensure a robust system that not only meets regulatory standards but also significantly elevates the quality of care delivered to patients.
Introduction
The rapid evolution of healthcare technology is fundamentally transforming the delivery of medical care, with the market for medical applications projected to surge to $760 billion by 2024. As healthcare organizations aim to enhance patient outcomes and streamline operations, grasping the essential features of medical software becomes imperative. What key functionalities can empower healthcare providers to adeptly navigate this intricate landscape? This article explores ten indispensable features of medical software that not only drive operational efficiency but also ensure compliance, elevate patient engagement, and facilitate seamless data exchange.
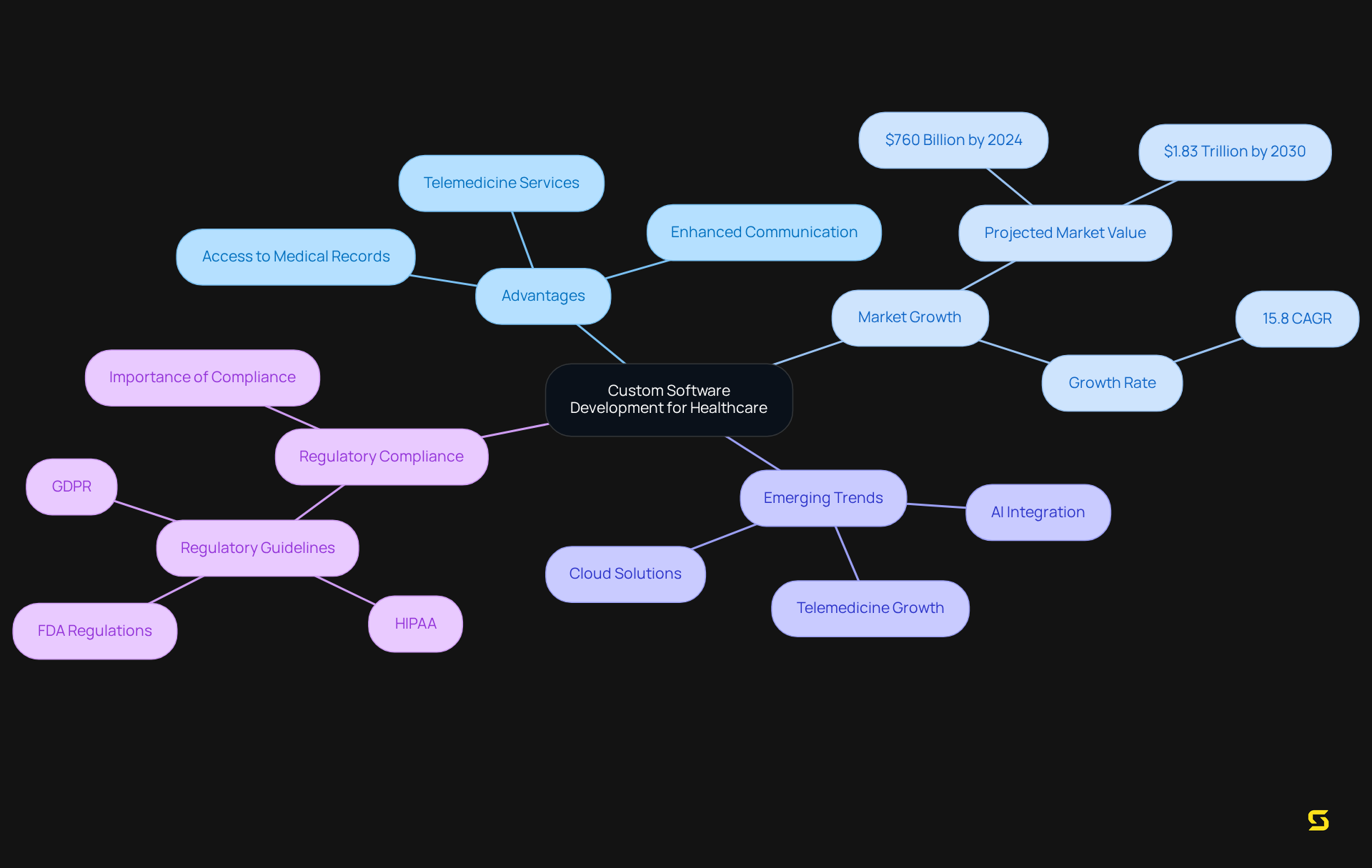
SDA: Custom Software Development for Healthcare Providers
SDA stands at the forefront of custom software development tailored for medical practitioners, delivering innovative solutions that dramatically enhance care and optimize operational processes. By leveraging advanced technologies alongside a user-centric design approach, SDA empowers medical organizations to adeptly manage their workflows and elevate patient outcomes. With profound insights into the distinct challenges encountered by medical service providers, SDA offers solutions that are not only functional but with their business objectives.
The medical application sector is projected to reach $760 billion by 2024, exhibiting an impressive growth rate of 15.8% CAGR. This surge underscores the escalating demand for effective digital solutions that bolster healthcare and operational efficiency. Custom software development yields numerous advantages, including:
- Improved access to medical records
- Enhanced communication among medical professionals
- Facilitation of telemedicine services
For instance, a recent initiative featuring a generative AI-powered medical management system resulted in a 20% increase in physician productivity and a 15% improvement in patient care efficiency. Moreover, an IoT-enabled telehealth solution for seniors enabled healthcare professionals to access real-time health data, significantly enhancing the quality of care for this demographic.
Emerging trends in medical application development for 2025 encompass:
- Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for predictive analytics
- Growing prominence of telemedicine
- Accelerated adoption of cloud-based solutions
These innovations are reshaping the operational landscape for medical providers, empowering them to deliver more efficient and effective care.
Experts in medical technology emphasize the critical importance of regulatory compliance in the development of medical applications, as it ensures safety and quality. As one expert aptly stated, "Regulatory compliance isn’t merely a legal obligation—it’s essential for creating safe, effective, and high-quality medical applications." By adhering to guidelines set forth by regulatory bodies, SDA assists clients in circumventing legal challenges and upholding a robust reputation within the industry. In summary, SDA's unwavering commitment to crafting tailored technological solutions enables medical practitioners to effectively navigate obstacles and enhance care for individuals.
Interoperability: Seamless Data Exchange Across Systems
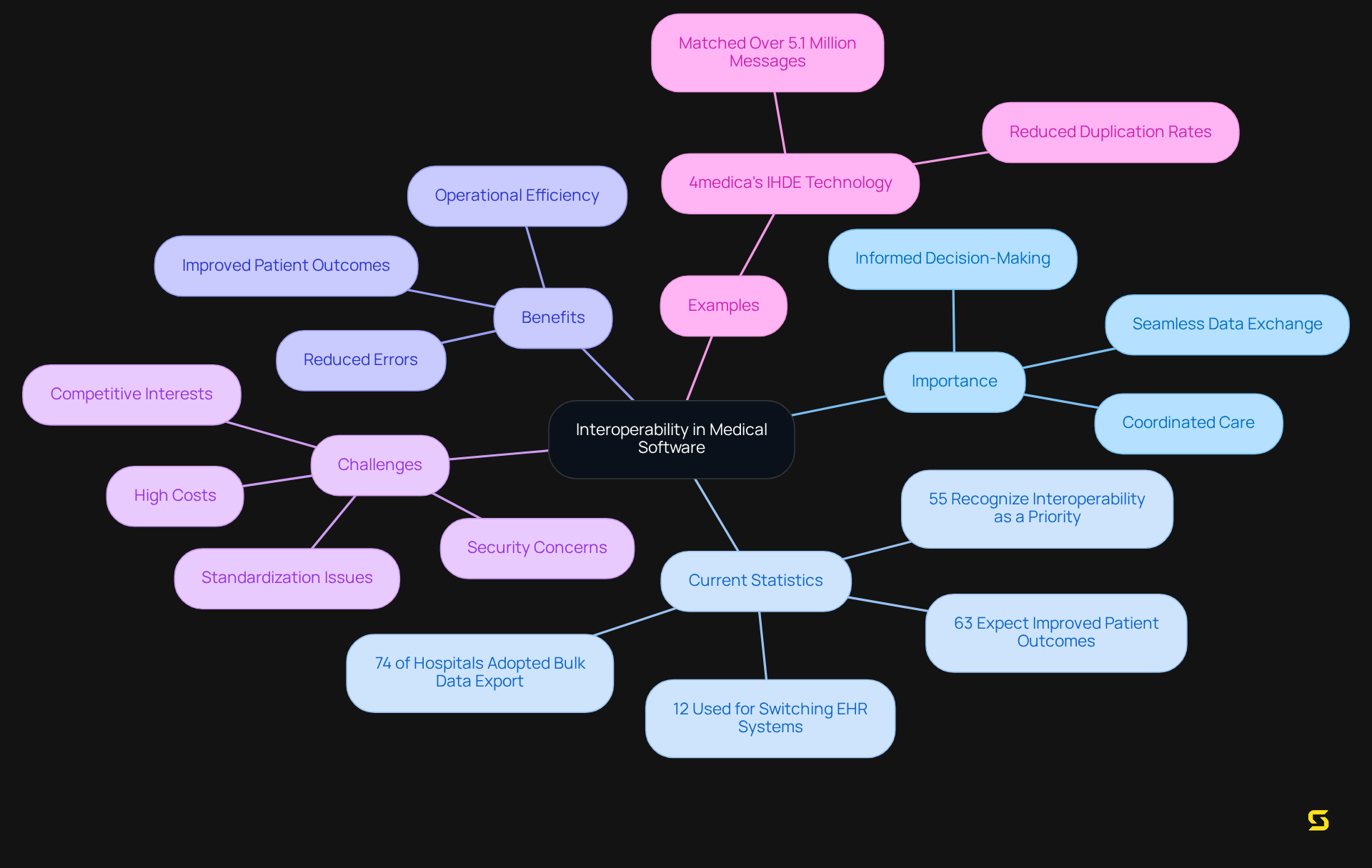
Interoperability in medical software is crucial for enabling seamless data exchange among various medical systems, such as Electronic Health Records (EHRs), laboratory systems, and billing software. This integration ensures that medical professionals have access to comprehensive and accurate individual information, which is critical for informed decision-making and coordinated care.
By enhancing interoperability through medical software, medical organizations can significantly reduce errors, improve patient outcomes, and boost overall operational efficiency. As of 2021:
- Only 74% of hospitals had adopted bulk data export technology.
- Merely 12% utilized it for switching EHR systems, underscoring a pressing need for advancements in this area.
Furthermore:
- Nearly 63% of medical professionals anticipate improved patient results through enhanced medical software interoperability.
- 55% of medical organizations recognize the adoption of medical software interoperability as a key priority.
However, challenges such as standardization, high costs, competitive interests, and security concerns continue to impede progress. A notable example of successful interoperability implementation is 4medica's IHDE technology, which matched over 5.1 million messages and significantly reduced duplication rates.
While improved data sharing offers various advantages, it also introduces potential risks, such as privacy violations and cybersecurity threats, which medical providers must carefully evaluate. The ongoing evolution of interoperability solutions is expected to play a pivotal role in by 2025, establishing it as a top priority for organizations seeking to enhance care quality and operational effectiveness.
User-Friendly Interface: Enhancing Usability for Healthcare Staff
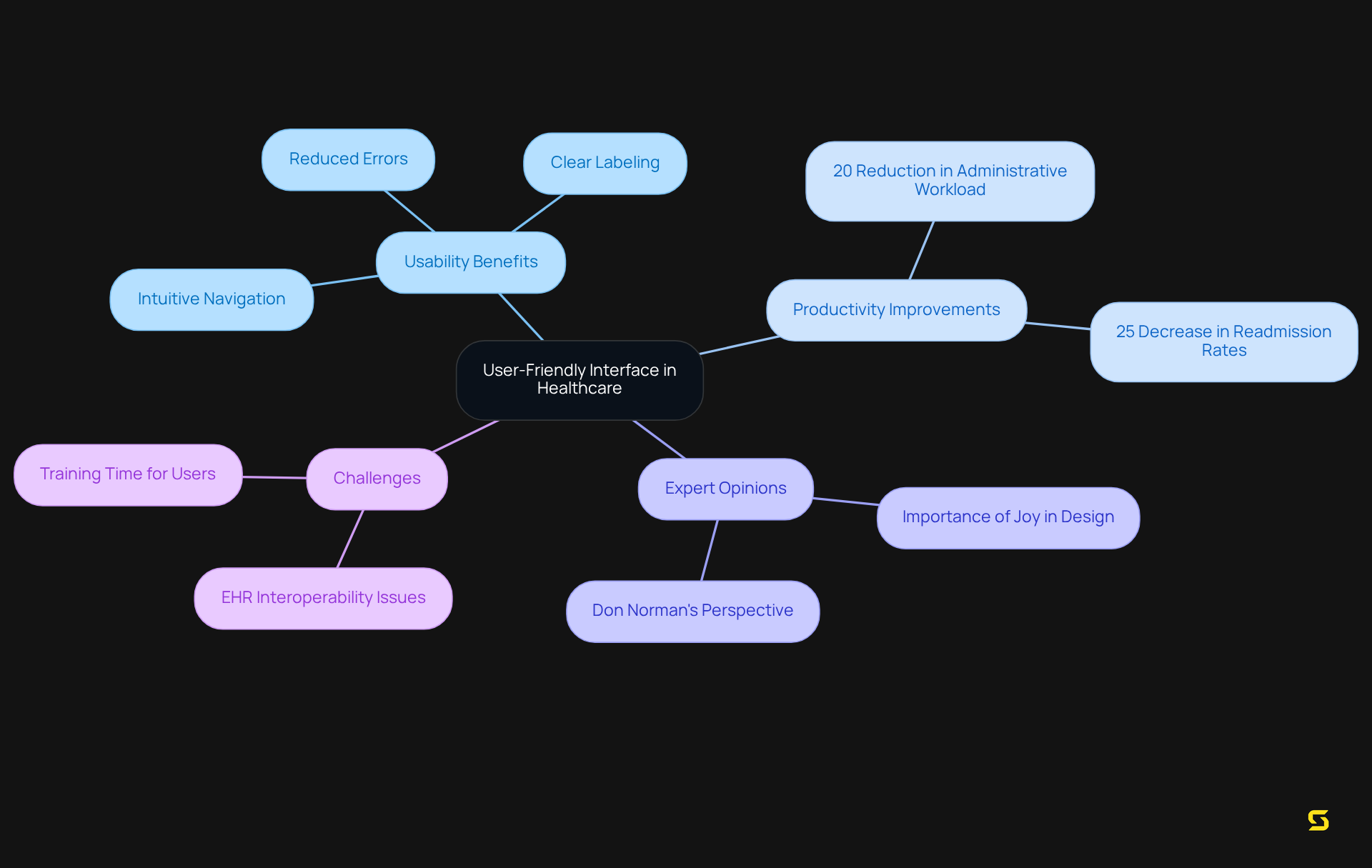
An easy-to-use interface is essential for [medical software applications](https://blog.sda.company/10-marketplace-trends-shaping-the-future-of-saa-s-solutions), significantly enhancing usability for medical personnel. Intuitive navigation, clear labeling, and accessible functionalities empower users to complete tasks efficiently, thereby reducing the time spent on administrative duties. This emphasis on usability not only boosts productivity but also minimizes the risk of errors associated with complex systems.
For instance, medical organizations that have adopted [user-friendly technology solutions](https://media.market.us/electronic-health-records-statistics) report notable improvements in staff productivity, with some experiencing up to a 20% reduction in administrative workload. Furthermore, the integration of big data analytics in Electronic Health Records (EHRs) has led to a 25% decrease in hospital readmission rates, underscoring the broader impact of usability on medical efficiency.
By prioritizing usability, the overall experience for both staff and users can be transformed by medical software, resulting in enhanced care delivery and operational efficiency. As usability expert Don Norman aptly states, "It is not enough that we build products that function, that are understandable and usable; we also need to build products that bring joy and excitement, pleasure and fun, and, yes, beauty to people’s lives."
This perspective reinforces the idea that ; it is about creating systems that facilitate seamless interactions, ultimately benefiting care professionals and their patients. Moreover, with 95% of non-federal acute care hospitals in the U.S. implementing EHR systems, the demand for user-friendly interfaces is more critical than ever, especially considering that 53% of medical practitioners face challenges with EHR interoperability.
Data Security: Protecting Patient Information and Compliance
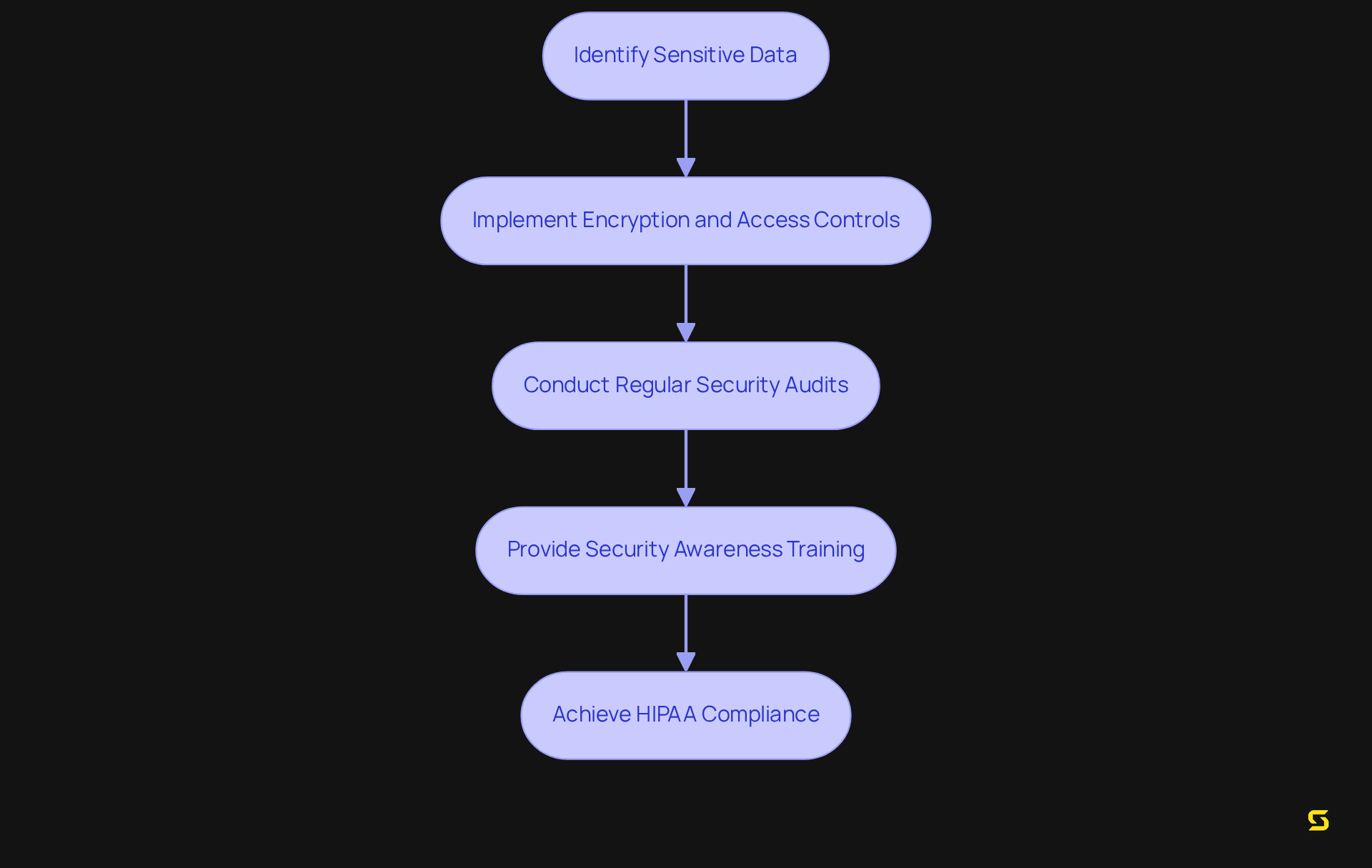
Data security is paramount in medical applications, safeguarding sensitive patient information from unauthorized access and breaches. Medical service providers must adhere to regulations such as HIPAA, necessitating the use of [medical software solutions](https://blog.sda.company/10-benefits-of-nearshore-application-development-for-saa-s-success) that encompass robust encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. In 2023, the average cost of a medical data breach surged to $10.93 million, marking a 10% increase from previous years and highlighting the financial ramifications of non-compliance.
Moreover, statistics reveal that 90% of cyber incidents stem from human error or behavior, underscoring the urgent need for ongoing security awareness training for medical personnel. By implementing comprehensive security measures, medical organizations can protect individual information, uphold trust, and avert the costly penalties associated with data breaches.
Notably, medical software solutions that ensure not only secure personal information but also enhance operational efficiency, making them indispensable in today’s medical landscape. As cybersecurity specialist Steve Alder emphasizes, "It is crucial that all employees undergo continuous security awareness training for two reasons," reinforcing the significance of robust security measures in mitigating risks and preserving the integrity of sensitive data in an increasingly digital environment.
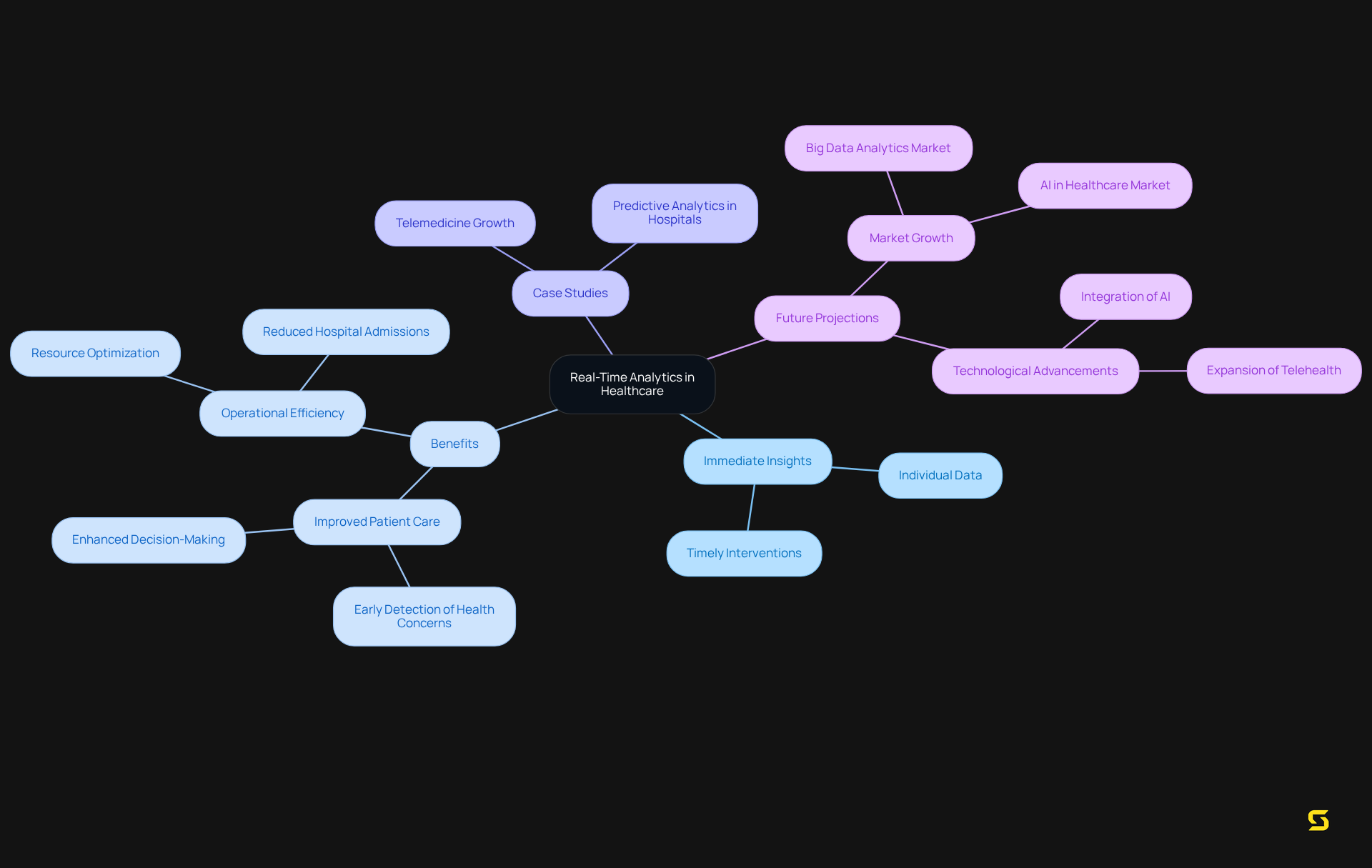
Real-Time Analytics: Immediate Insights for Better Patient Care
Medical software with real-time analytics empowers medical professionals by providing immediate insights into individual data, facilitating timely interventions and informed decision-making. By analyzing data as it is generated, medical organizations can swiftly identify trends, monitor individual conditions, and optimize resource allocation. This capability not only enhances care for individuals but also significantly improves .
For instance, hospitals utilizing real-time analytics have reported a 25% decrease in hospital admissions for chronic disease management, showcasing the tangible benefits of immediate insights (source: Telemedicine Growth case study). Furthermore, medical analysts emphasize that the incorporation of real-time information can lead to better outcomes for individuals, with predictive analytics facilitating early detection of potential health concerns.
According to Statista, the global big data analytics market for clinical analysis is projected to reach $11.35 billion by 2025, underscoring the growing importance of these technologies. As we approach 2025, the advantages of real-time information in medical software will become increasingly evident, reinforcing its status as a critical component of contemporary health applications.
EHR Integration: Comprehensive Patient Management Solutions
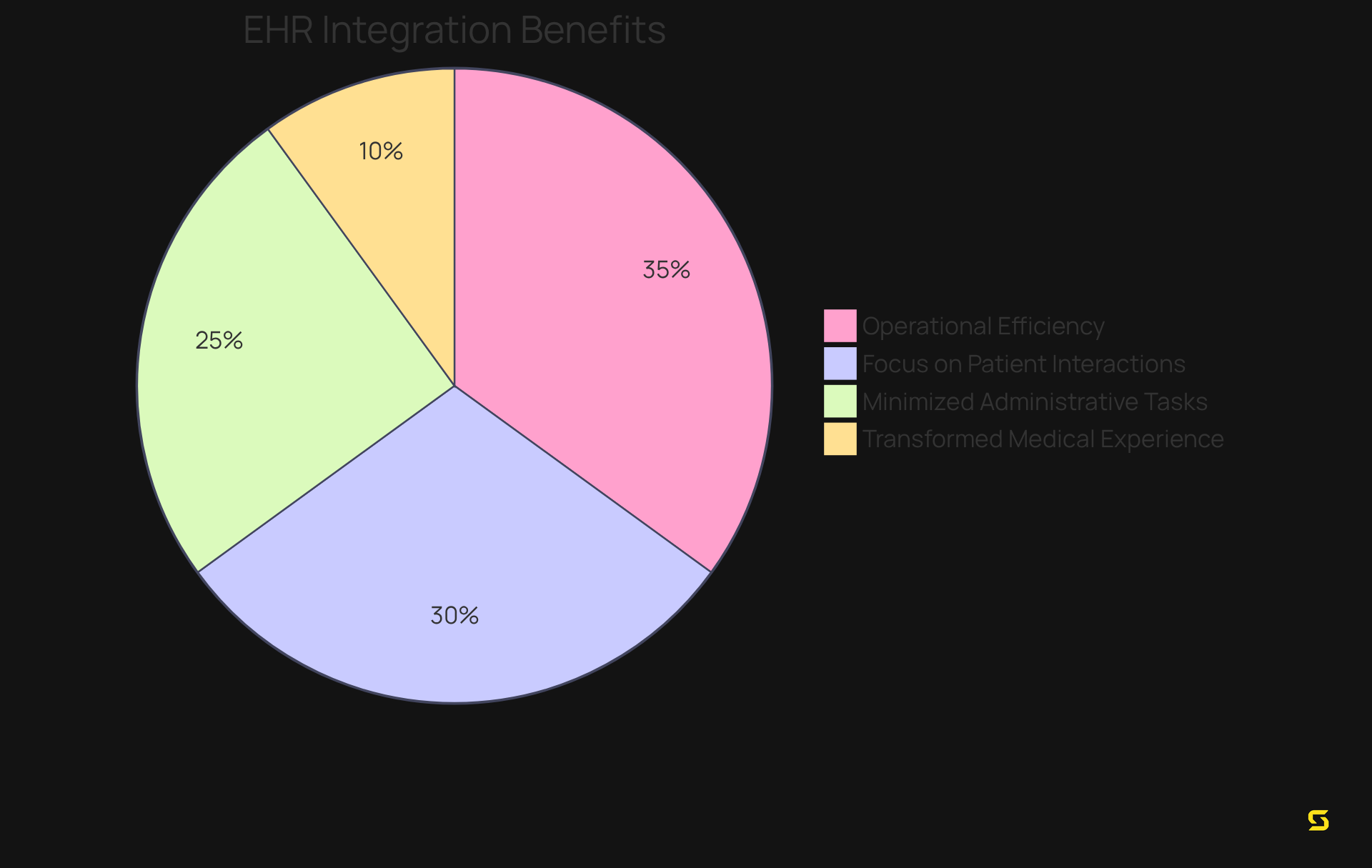
EHR integration stands as a pivotal element of medical software, equipping providers with robust management solutions for individuals. By seamlessly connecting with existing EHR systems, medical software enhances workflows, fosters improved communication, and guarantees that all pertinent individual information remains readily accessible. This integration not only but also minimizes redundant efforts, significantly elevating health outcomes.
As industry specialists underscore, the ability to access comprehensive medical histories empowers clinicians to make swift, informed decisions, ultimately enhancing the quality of care delivered. Looking ahead to 2025, the emphasis on EHR integration will continue to intensify, as medical providers increasingly recognize its potential to streamline operations and elevate care standards.
The benefits of such integration are unmistakable:
- It enhances operational efficiency
- It allows medical professionals to focus more on patient interactions rather than administrative tasks
- It transforms the overall medical experience
Telemedicine Features: Expanding Access to Healthcare Services
The telemedicine capabilities in medical software are essential for broadening access to medical services, especially for individuals who face challenges in reaching healthcare facilities. Key functionalities include:
- Video conferencing
- Secure messaging
- Remote monitoring tools
These features facilitate effective communication and care delivery. By integrating telemedicine capabilities into their operations, medical organizations can significantly enhance client engagement, improve access to specialists, and reduce appointment wait times using medical software.
A recent survey revealed that:
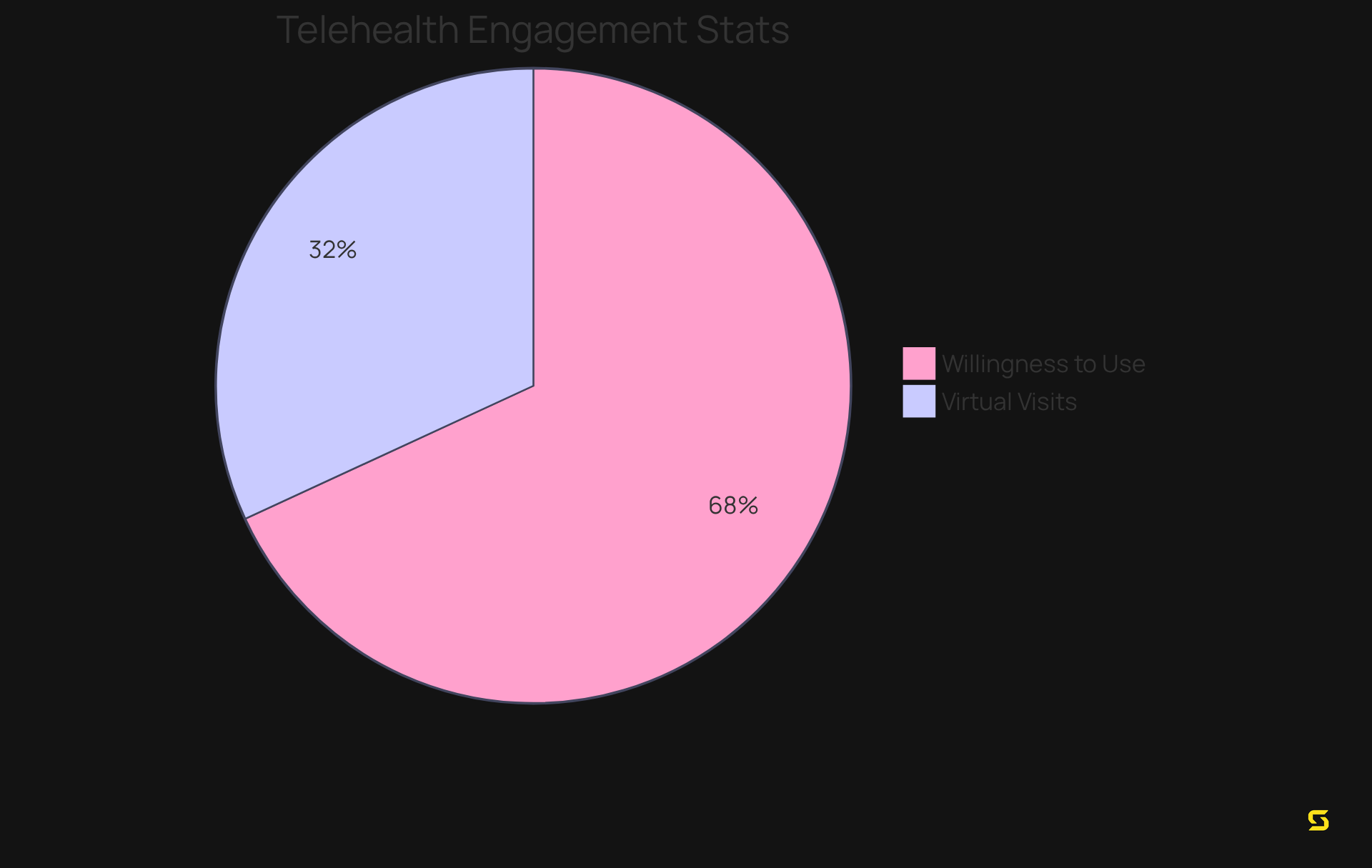
- 44% of individuals had a virtual visit in the past year
- 94% expressed a willingness to use telehealth services again—underscoring the convenience and effectiveness of these solutions.
Furthermore, the U.S. telehealth market size was valued at $42.54 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 23.8% from 2025 to 2030, reflecting the increasing reliance on remote consultation tools.
As medical professionals embrace these technologies, including remote monitoring (RPM) systems, they not only enhance access for individuals but also optimize operations, ultimately resulting in improved health outcomes. To leverage these advancements, SaaS product owners must consider incorporating into their medical software solutions, ensuring they meet the evolving needs of both medical professionals and patients.
Customizable Workflows: Tailoring Software to Operational Needs
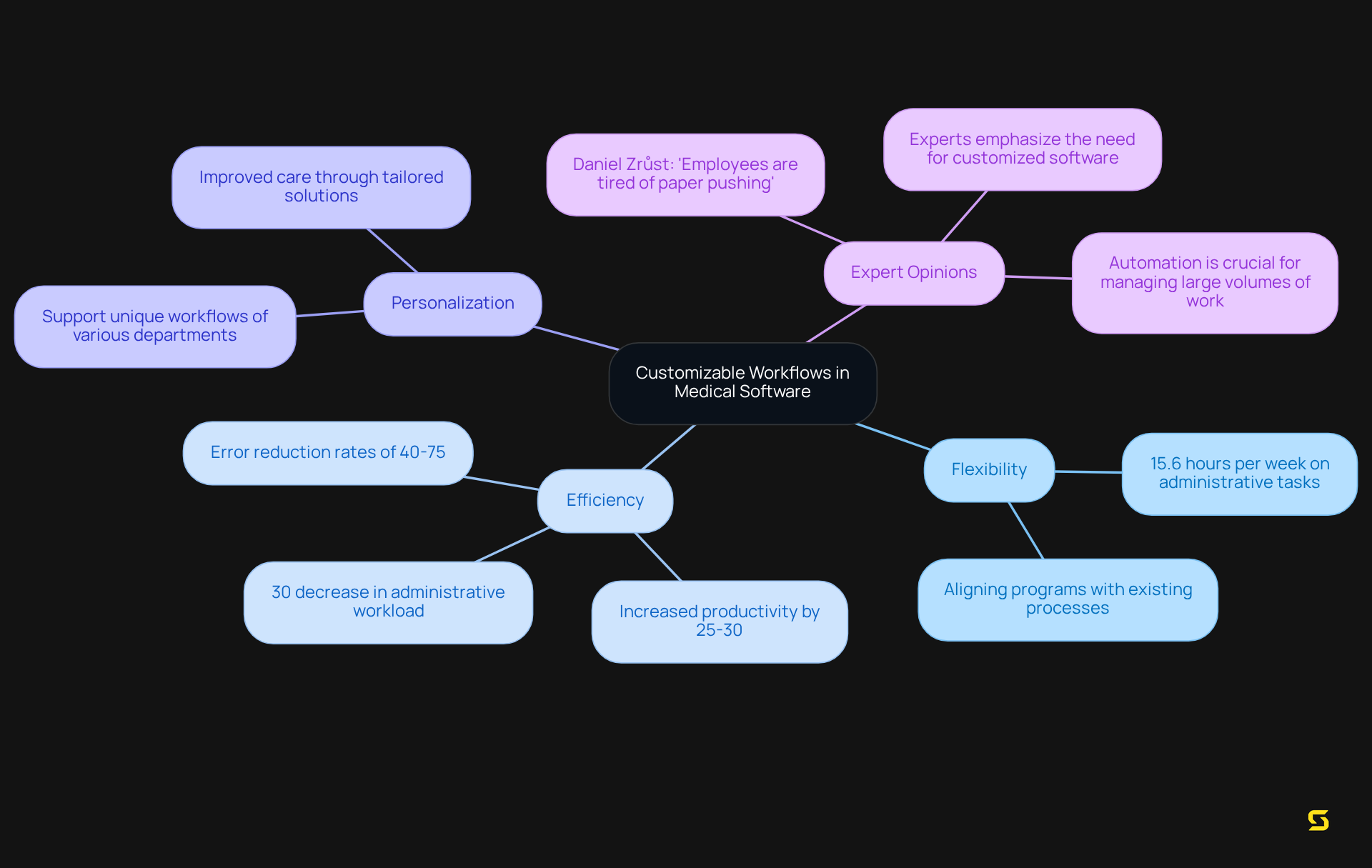
Customizable workflows in medical software empower medical organizations to adapt systems to their specific operational requirements. This flexibility not only allows providers to align programs with existing processes but also significantly enhances efficiency and user satisfaction. By facilitating personalization, medical applications effectively support the unique workflows of various departments, resulting in improved care and streamlined operations.
For instance, a hospital that implemented customized software solutions reported a remarkable 30% decrease in administrative workload, enabling staff to focus more on interactions with individuals receiving care. Experts in medical operations emphasize that customized approaches to medical software are essential for boosting the efficiency of technology in clinical environments, ultimately leading to better outcomes for both practitioners and patients.
Furthermore, with medical providers dedicating approximately 15.6 hours a week to administrative tasks, alleviating this burden through automation is crucial. As industry specialists assert, "At its essence, workflow automation in the medical field signifies utilizing technology to manage routine, repeatable tasks to enhance efficiency in medical operations." This statement underscores the pivotal role of customizable workflows in and data accuracy.
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting Healthcare Standards and Regulations
Regulatory compliance stands as a cornerstone of medical applications, ensuring that medical organizations meet essential industry standards and legal mandates. Adherence to regulations such as HIPAA is non-negotiable, as it oversees the privacy and security of individual information. By incorporating compliance features into their software solutions, medical providers can significantly minimize risks related to data breaches, which have incurred an average cost of $4.88 million per incident in 2024. This proactive strategy not only aids in but also promotes patient trust—an essential component for successful medical operations.
Legal experts emphasize the critical nature of adhering to HIPAA standards for medical applications. Organizations that implement robust compliance measures can save an average of $2.03 million by integrating data security with privacy functions. Moreover, 90% of compliance leaders anticipate a 30% rise in compliance costs, underscoring the urgent need for effective compliance strategies in the evolving healthcare landscape.
Examples of medical applications that successfully meet HIPAA standards include:
- Platforms offering secure messaging solutions
- Robust data encryption features
These tools not only enhance operational efficiency but also guarantee that data remains safeguarded against unauthorized access. As medical regulations continue to evolve, the incorporation of compliance elements in clinical applications will be essential for practitioners striving to uphold high standards of care while protecting sensitive information.
Patient Engagement Tools: Enhancing Communication and Interaction
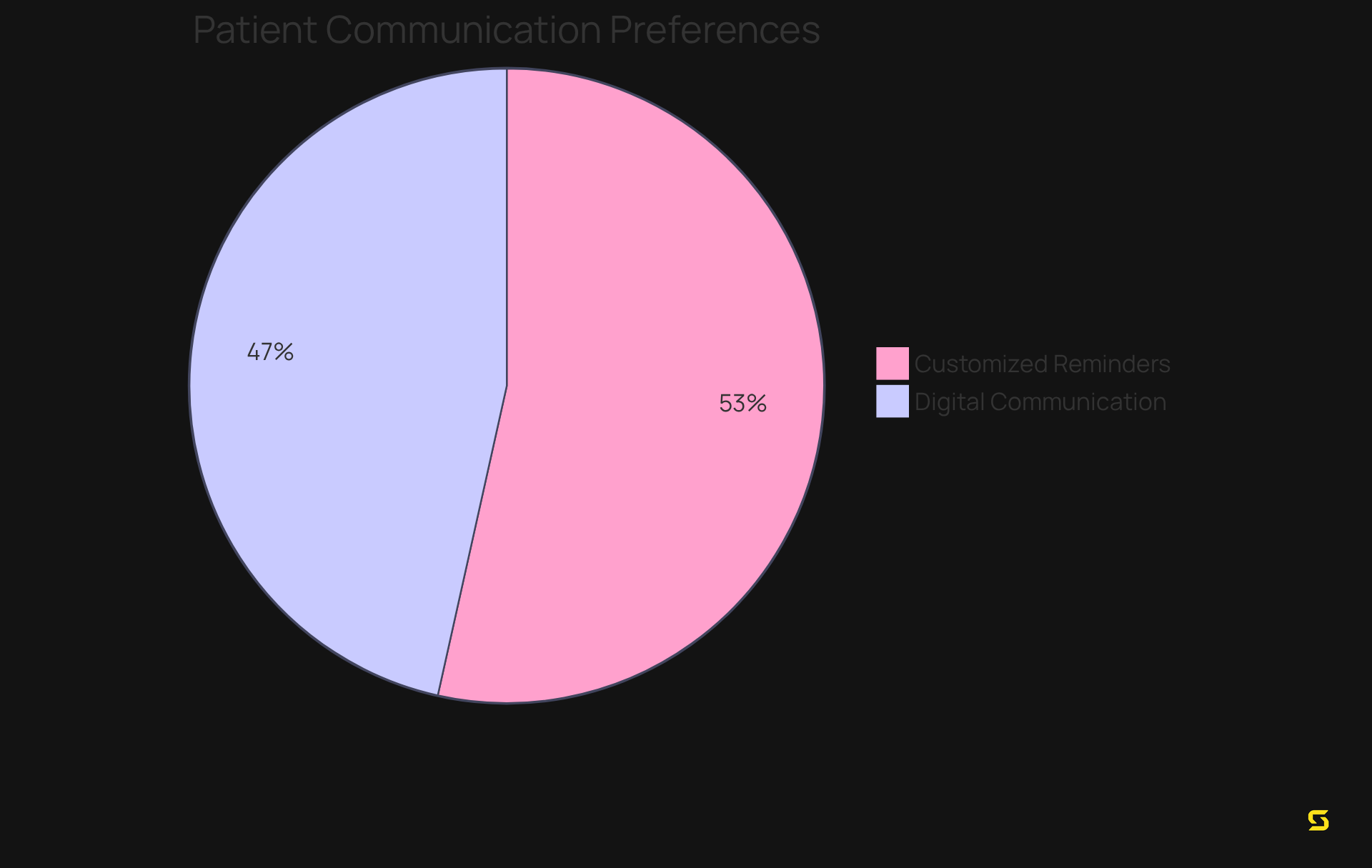
Engagement tools in medical software are crucial for enhancing communication and interaction between practitioners and individuals seeking care. Secure messaging, tailored appointment reminders, and access to educational materials empower individuals to actively participate in their wellness journey. Notably, 92% of individuals expect customized reminders and communications from their medical practitioners, underscoring a significant demand for personalized care. Furthermore, 80% of individuals prefer digital communication channels for appointment reminders and follow-ups, reflecting a substantial shift in expectations.
By fostering a collaborative relationship, as highlighted by Klas Research, individuals who describe their relationship with their medical professionals as 'collaborative' are three times more likely to value technology-assisted communications. Ultimately, through medical software not only enhances the experiences of individuals but also contributes to better health outcomes, making it indispensable in modern medical practices.
To optimize the effectiveness of these tools, healthcare providers must prioritize personalization and digital communication strategies in their patient engagement initiatives.
Conclusion
The exploration of essential features in medical software for healthcare providers unveils a transformative landscape where technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing patient care and operational efficiency. By emphasizing customizable workflows, interoperability, user-friendly interfaces, and robust data security, healthcare organizations can markedly improve their service delivery and patient outcomes.
Key insights from this discussion underscore the necessity of integrating telemedicine features, real-time analytics, and regulatory compliance into medical software solutions. These elements not only streamline processes but also cultivate improved communication between healthcare providers and patients, ultimately resulting in better health outcomes. The projected growth of the medical application sector highlights the urgency for healthcare providers to embrace these advancements to remain competitive and meet evolving patient expectations.
As the healthcare industry progresses towards 2025, adopting these essential functionalities will be crucial for organizations striving to enhance their operational capabilities and deliver high-quality care. By prioritizing the implementation of innovative medical software solutions, healthcare providers can effectively navigate challenges and ensure a patient-centered approach that aligns with the future of healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is SDA and what services do they provide for healthcare providers?
SDA specializes in custom software development for healthcare providers, offering innovative solutions that enhance care and optimize operational processes. They focus on user-centric design and advanced technologies to help medical organizations manage workflows and improve patient outcomes.
What are the projected trends in the medical application sector?
The medical application sector is projected to reach $760 billion by 2024, with a growth rate of 15.8% CAGR. Key trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, the rise of telemedicine, and the accelerated adoption of cloud-based solutions.
How does custom software development benefit healthcare providers?
Custom software development provides several advantages, such as improved access to medical records, enhanced communication among medical professionals, and facilitation of telemedicine services.
Can you provide an example of the impact of custom software in healthcare?
A recent initiative featuring a generative AI-powered medical management system resulted in a 20% increase in physician productivity and a 15% improvement in patient care efficiency.
What is interoperability in medical software and why is it important?
Interoperability refers to the seamless data exchange among various medical systems, such as EHRs, laboratory systems, and billing software. It is crucial for informed decision-making and coordinated care, helping to reduce errors and improve patient outcomes.
What challenges does interoperability face in the medical field?
Challenges include standardization, high costs, competitive interests, and security concerns, which impede progress in achieving effective interoperability.
What are the benefits of a user-friendly interface in medical software?
A user-friendly interface enhances usability for medical personnel, reduces administrative workload, and minimizes the risk of errors. Organizations that prioritize usability report significant improvements in staff productivity and patient care efficiency.
How has usability impacted hospital readmission rates?
The integration of big data analytics in EHRs, which emphasizes usability, has led to a 25% decrease in hospital readmission rates.
What percentage of non-federal acute care hospitals in the U.S. have implemented EHR systems?
95% of non-federal acute care hospitals in the U.S. have implemented EHR systems, highlighting the critical demand for user-friendly interfaces in healthcare technology.





