Overview
This article delves into the diverse types of cloud computing—public, private, hybrid, and community—alongside their respective service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. By highlighting their applications across various sectors, it underscores how these models address specific business needs, enhance operational efficiency, and drive innovation in industries such as:
- Healthcare
- E-commerce
- Education
- Finance
- Startups
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage cloud solutions effectively. Embrace the potential of cloud computing to transform your business landscape.
Introduction
Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed how organizations access and utilize technology, evolving traditional IT infrastructure into dynamic, scalable solutions. With a diverse array of deployment and service models available, businesses can customize their cloud strategies to align with specific operational needs and compliance requirements.
Yet, as companies navigate this intricate landscape, a pressing question arises: which type of cloud computing is best suited to address their unique challenges and goals?
This article explores the distinct types of cloud computing, their applications, and the critical considerations organizations must evaluate to fully harness the potential of the cloud.
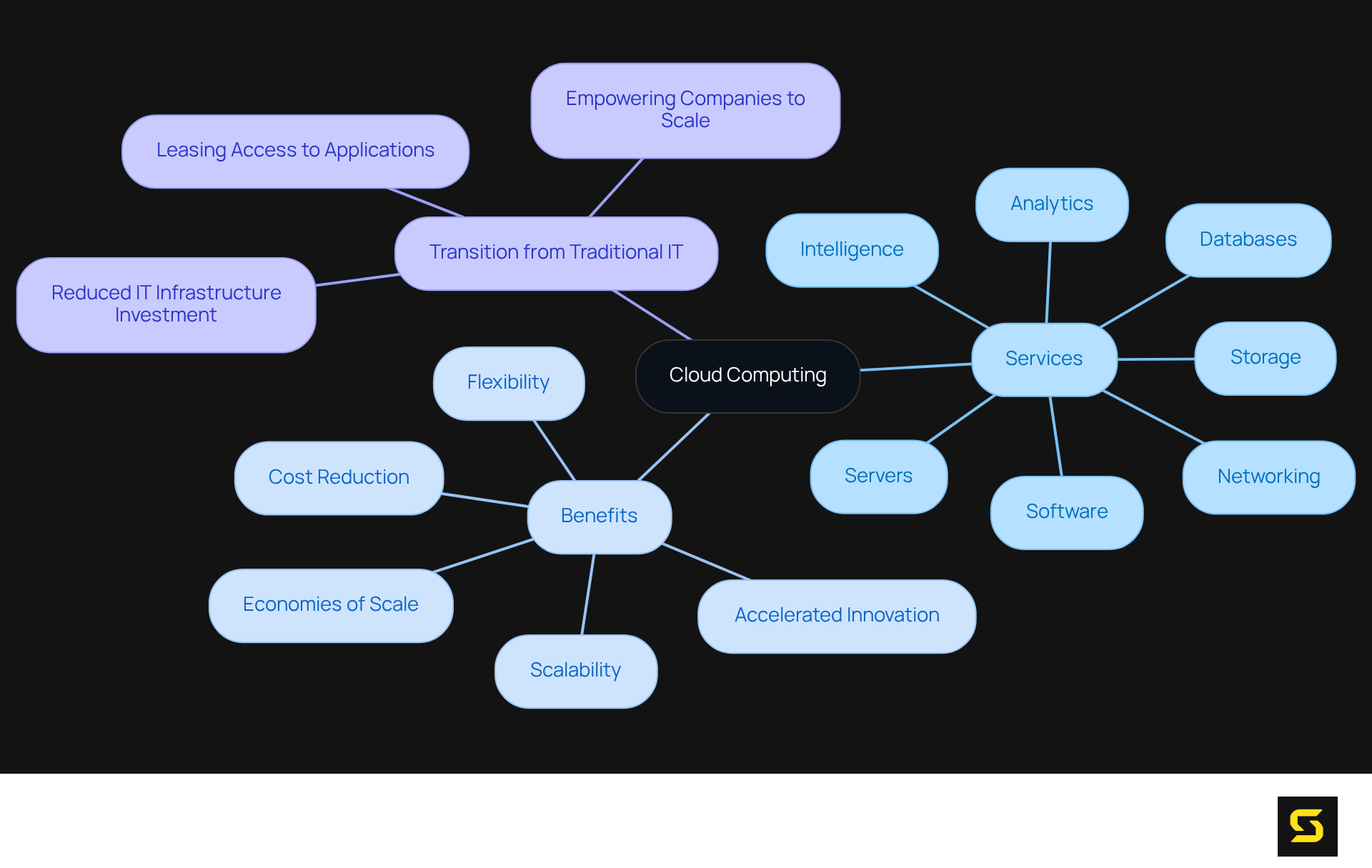
Define Cloud Computing
Cloud technology represents a revolutionary shift in the delivery of information services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—via the internet, commonly referred to as 'the cloud.' This innovative model not only facilitates flexible resource allocation but also accelerates innovation and drives economies of scale.
Organizations no longer need to invest heavily in their own IT infrastructure or data centers; instead, they can lease comprehensive access to applications and storage from service providers. This significant transition from traditional on-site systems to various types of has fundamentally transformed business operations, empowering companies to scale efficiently while substantially reducing expenses.
Embrace the cloud and unlock the potential for your organization to thrive in an increasingly digital landscape.
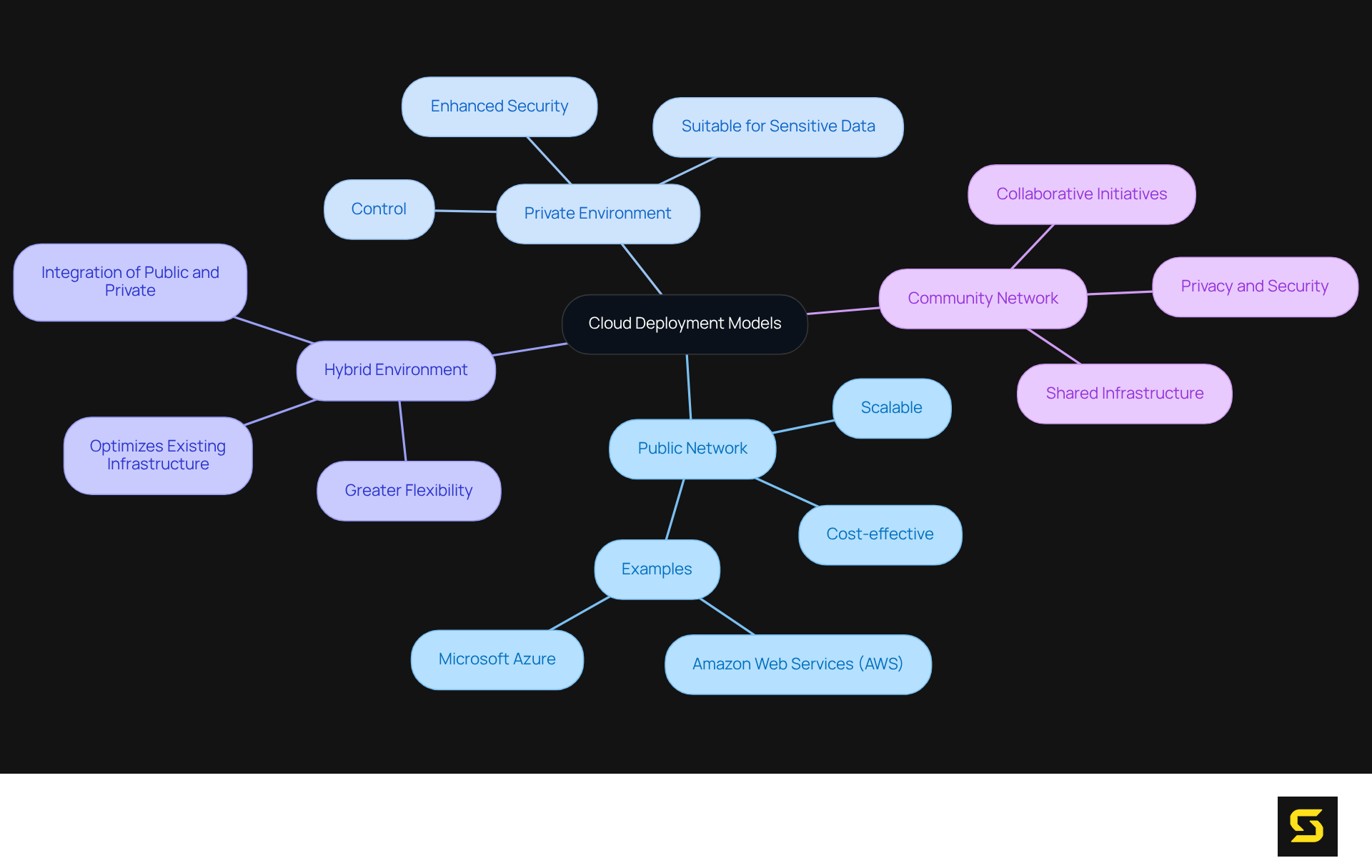
Explore Cloud Deployment Models
Computing services can be leveraged in diverse ways, which are primarily categorized into four types of cloud computing: public, private, hybrid, and community infrastructures.
- Public Network: Services are delivered via the public internet, shared among various organizations. This model is cost-effective and scalable, making it particularly advantageous for small to medium-sized enterprises. Notable examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
- Private Environment: This framework is exclusively dedicated to a single organization, offering enhanced security and control. It is particularly suitable for businesses that face stringent regulatory requirements or manage sensitive data.
- Hybrid Environment: By integrating both public and private infrastructures, this approach facilitates the exchange of data and applications between them. It provides greater flexibility and optimizes existing infrastructure.
- Community Network: This framework is shared among multiple organizations with similar interests or needs, fostering collaborative initiatives while ensuring privacy and security.
Each of the types of cloud computing presents distinct advantages and is selected based on specific business needs and compliance requirements. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for organizations aiming to .
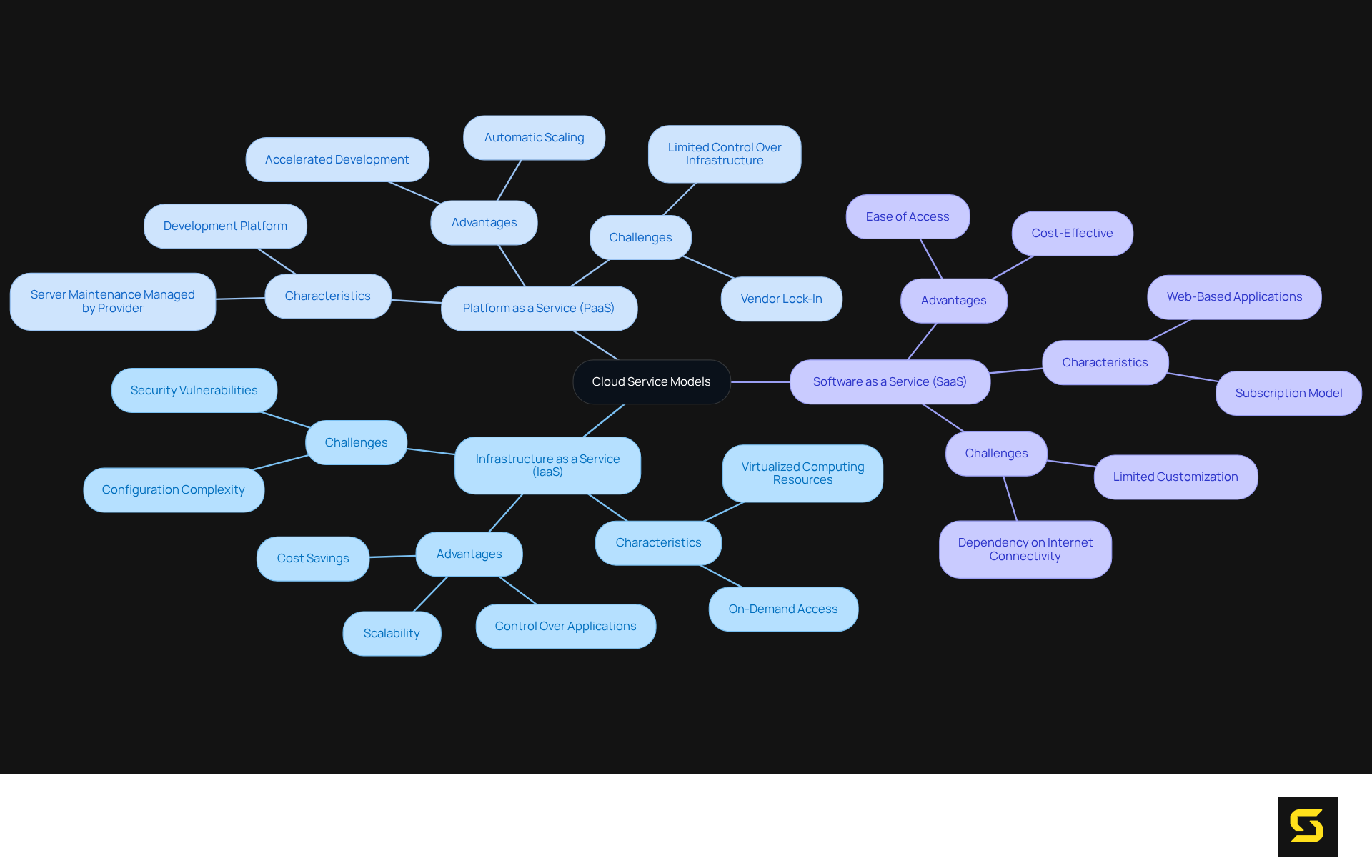
Examine Cloud Service Models
Online services are fundamentally categorized into three primary types of cloud computing: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This robust framework delivers virtualized computing resources through the internet, enabling users to rent servers, storage, and networking capabilities. Such flexibility empowers organizations to construct and manage their own IT infrastructure without the encumbrance of physical hardware. Notable examples, including Google Cloud Platform and DigitalOcean, showcase scalable solutions tailored to diverse business needs. However, it is imperative for organizations to configure IaaS correctly, as improper setup can lead to performance issues and security vulnerabilities.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a comprehensive platform for customers to develop, run, and manage applications, alleviating the complexities associated with infrastructure management. This framework is particularly advantageous for developers aiming to accelerate application development, as it simplifies the process by overseeing server maintenance and scaling. Platforms such as Heroku and Red Hat OpenShift exemplify how PaaS can enhance productivity and reduce time to market, rendering it a compelling choice for both startups and established enterprises. Nonetheless, organizations should remain cognizant of potential challenges, including vendor lock-in and limited control over the underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS provides software applications via the internet, allowing users to access them through web browsers without the necessity for installation or maintenance. This model is not only convenient but also cost-effective, transferring expenses from capital expenditures to operational expenditures. Widely recognized SaaS applications, such as Salesforce and Dropbox, demonstrate the ease of use and accessibility this approach affords. As of 2025, approximately 70% of businesses are projected to utilize SaaS solutions, underscoring its increasing prevalence in the market. However, businesses may encounter challenges related to limited customization and reliance on internet connectivity.
Understanding the types of cloud computing service models is essential for organizations to that align with their operational requirements and strategic objectives, ensuring they harness the full potential of cloud technology.
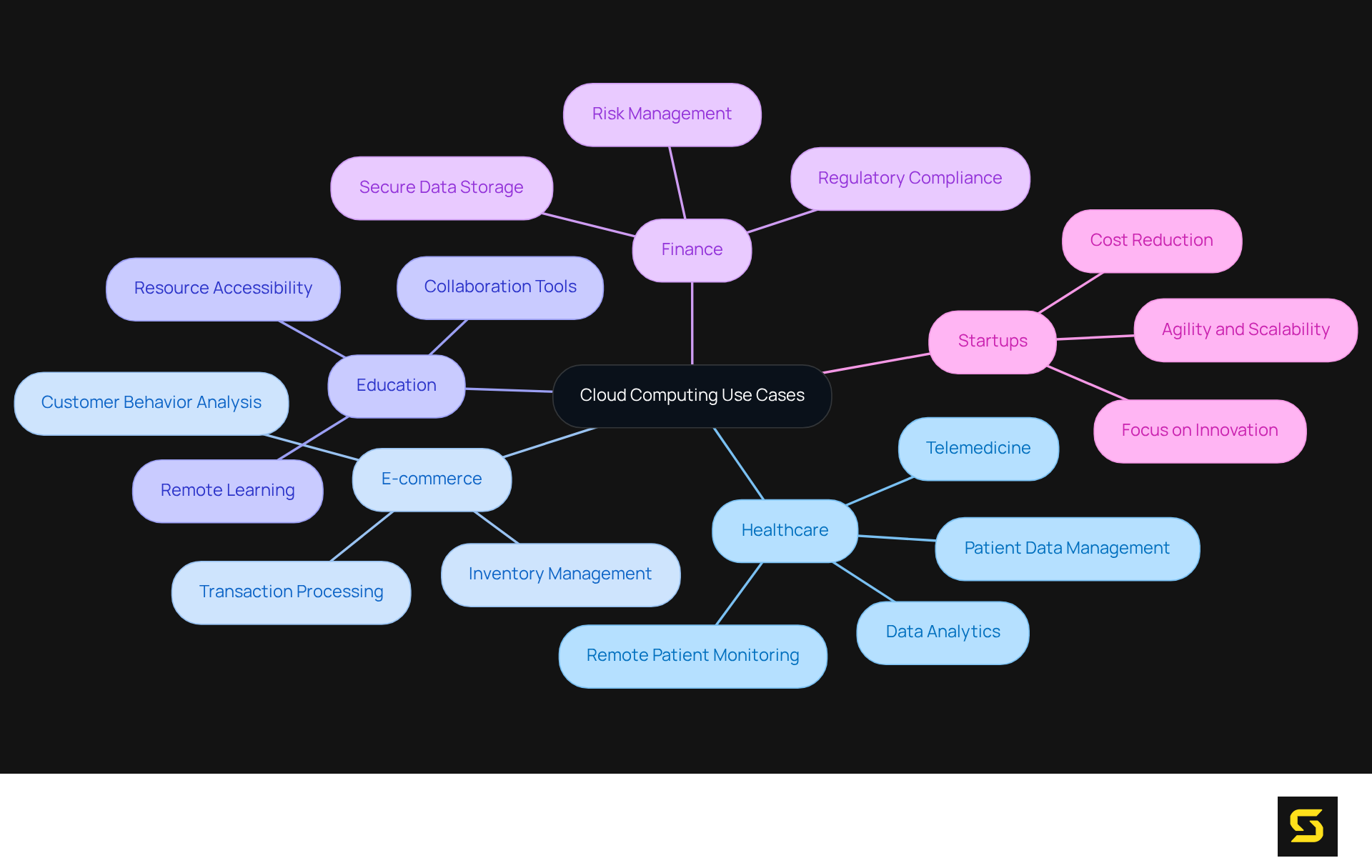
Identify Cloud Computing Use Cases
Internet-based processing has emerged as a transformative influence across various sectors, showcasing its adaptability and efficacy in enhancing operational efficiency and fostering innovation. Key applications include:
- Healthcare: Cloud computing empowers healthcare providers to securely store and share patient data, facilitating telemedicine and improving patient care through advanced data analytics. For instance, platforms like Cerner HealtheIntent analyze large datasets to identify patterns in patient care, leading to better health outcomes and reduced costs. Significantly, over 80% of healthcare organizations are utilizing public providers, which is anticipated to enhance patient satisfaction and operational efficiency.
- E-commerce: Online retailers leverage internet services to manage inventory, process transactions, and analyze customer behavior. This not only enhances user experience but also streamlines operations. Businesses employing online solutions report substantial improvements in transaction processing speed and inventory management efficiency. For example, cloud-based systems allow retailers to automate inventory management, leading to reduced stockouts and improved customer satisfaction.
- Education: Educational institutions utilize online platforms for remote learning, enabling students to access resources and collaborate from afar. This shift has made , accommodating diverse learning styles and schedules.
- Finance: Financial institutions employ online computing for secure data storage, risk management, and regulatory compliance. By embracing online solutions, these organizations can ensure efficient operations while protecting sensitive information from cyber threats.
- Startups: Numerous startups adopt online solutions to reduce initial expenses and quickly expand their operations. This allows them to focus on innovation rather than the complexities of infrastructure management, fostering a culture of agility and responsiveness.
These diverse use cases illustrate how the different types of cloud computing not only support operational efficiency but also catalyze growth and innovation across various sectors.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed how organizations manage their IT resources, presenting a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional infrastructure. By grasping the different types of cloud computing—public, private, hybrid, and community—businesses can customize their strategies to address specific operational needs and compliance requirements. This transition not only boosts efficiency but also cultivates innovation, empowering organizations to excel in a digital landscape.
The key arguments presented in this article underscore the distinct service models of cloud computing:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Each model offers unique benefits and challenges, catering to varied business needs. Furthermore, the article examines real-world applications across sectors such as healthcare, e-commerce, education, finance, and startups, illustrating the transformative influence of cloud technology on operational efficiency and growth.
The importance of adopting cloud computing cannot be overstated. As businesses navigate the complexities of modern technology, leveraging cloud solutions not only optimizes resource allocation but also drives innovation and competitive advantage. Organizations are urged to evaluate their specific needs and strategically implement cloud computing to unlock its full potential, ensuring they remain agile and responsive in an ever-evolving market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of information services, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, via the internet, known as 'the cloud.'
How does cloud computing benefit organizations?
Cloud computing allows organizations to avoid heavy investments in IT infrastructure or data centers by leasing access to applications and storage from service providers, leading to flexible resource allocation, accelerated innovation, and reduced expenses.
What has changed in business operations due to cloud computing?
The transition from traditional on-site systems to cloud computing has transformed business operations, enabling companies to scale efficiently and significantly cut costs.
Why is embracing cloud technology important for organizations?
Embracing cloud technology helps organizations unlock their potential to thrive in an increasingly digital landscape.





