Overview
The article delineates nine critical steps for achieving HIPAA compliance in SaaS products. These steps encompass:
- Conducting comprehensive risk analyses
- Implementing both administrative and technical safeguards
- Providing ongoing employee training
Evidence supports the necessity of:
- Structured policies
- Regular audits
- Remaining informed on regulatory changes
to effectively safeguard electronic protected health information (ePHI) and mitigate compliance risks. By adhering to these essential practices, organizations can not only protect sensitive data but also enhance their overall compliance posture. It is imperative to act decisively in implementing these measures to ensure robust protection and compliance.
Introduction
Navigating the labyrinth of HIPAA compliance presents a formidable challenge for SaaS providers, particularly as the healthcare landscape evolves and regulations tighten. With an impressive 92% of healthcare organizations now achieving compliance, the stakes have never been higher for those developing software solutions in this domain. This article delineates nine essential steps that not only facilitate adherence to HIPAA requirements but also bolster the security and trustworthiness of health information systems. How can organizations effectively implement these measures to safeguard sensitive data and avert costly penalties?
SDA: Custom Software Development for HIPAA Compliance
SDA stands at the forefront of tailored software development that adheres to health regulations such as HIPAA, empowering healthcare entities to securely manage protected health information (PHI). By leveraging advanced technologies and a user-centric design approach, SDA not only meets regulatory standards but also enhances the overall user experience.
As of March 5, 2024, a remarkable 92% of healthcare organizations have achieved regulatory compliance, underscoring a strong commitment to patient privacy and protection. This dedication to quality and regulatory adherence positions SDA as a trusted ally for healthcare providers and SaaS firms navigating the complexities of .
Successful projects, which illustrate enhanced customer relationships, underscore the effectiveness of implementing robust security measures—such as:
- encryption
- access controls
- regular audits of activities concerning the storage and transmission of PHI
By concentrating on these essential elements, SDA enables clients to cultivate trust and loyalty among their users, ultimately driving improved operational efficiency and a competitive edge in the healthcare sector.
Understand the HIPAA Security Rule
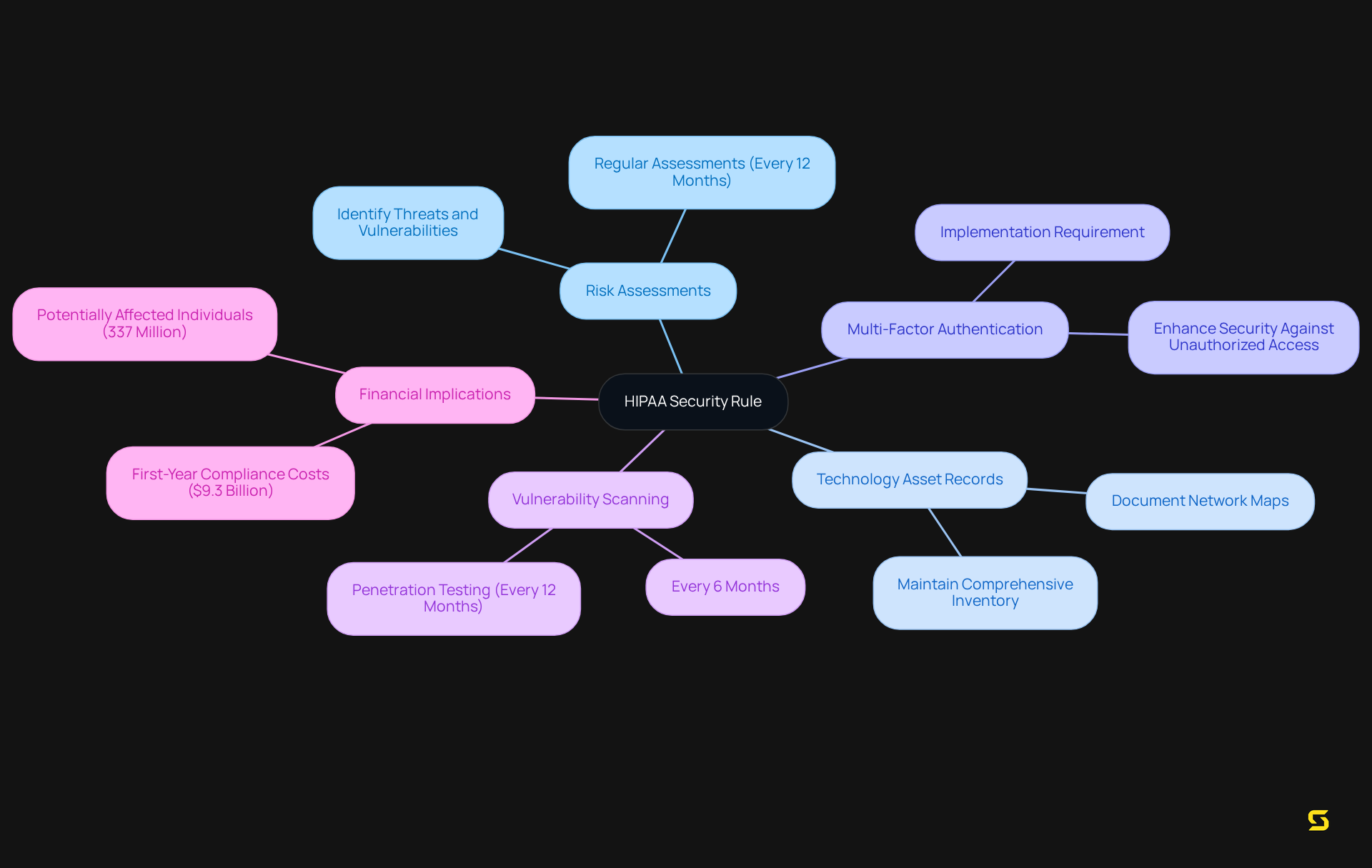
The HIPAA establishes national standards for protecting electronic protected health information (ePHI) through its Security Rule. It mandates that covered entities implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI. Understanding is critical for SaaS providers, as non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and loss of trust from clients and patients alike.
Key components of the HIPAA Security Rule include:
- The necessity for comprehensive risk assessments, which must identify potential threats and vulnerabilities to ePHI.
- Organizations are also required to keep a record of their technology assets and perform regular assessments of their protective measures at least once every 12 months.
- The implementation of multi-factor authentication and encryption for ePHI is now a critical expectation, reflecting the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
- The suggested mandate for vulnerability scanning every six months and penetration testing every 12 months is essential for upholding strong protective measures.
Current insights reveal that many SaaS providers still grapple with the challenges of HIPAA compliance. A recent analysis indicated that approximately 337 million individuals could be affected by regulatory changes, underscoring the widespread impact of these rules. Specialists in healthcare regulations emphasize that proactive measures, such as regular training and updates to security protocols, are vital for protecting ePHI effectively. As one expert noted, 'The evolving nature of cyber threats necessitates that organizations not only comply with existing regulations but also anticipate future challenges in data protection.'
Furthermore, the overall projected first-year expenses for regulated organizations and health plan sponsors to adhere to these regulations are around $9.3 billion, emphasizing the financial consequences of these requirements for SaaS providers. By prioritizing adherence to the Security Rule, SaaS providers can not only reduce risks but also enhance their reputation as reliable partners in the healthcare ecosystem.
Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Analysis
Carrying out a thorough risk assessment is not just crucial; it is imperative for protecting electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. This process involves evaluating potential threats, assessing the effectiveness of existing safeguards, and within the entity’s data management practices. In 2023, a staggering 553 large-scale breaches were reported, affecting over 109 million patients—a 98.9% increase from the previous year. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for comprehensive risk assessments.
Organizations must systematically determine the likelihood of vulnerabilities occurring and evaluate the potential impact on patient data. For instance, unauthorized access or disclosure of PHI accounted for 14.83% of breaches reported, highlighting a significant area of concern. By performing regular Risk Analyses (SRA), entities can not only fulfill the requirements of HIPAA but also create focused protective measures that effectively safeguard sensitive information.
Insights from cybersecurity experts such as Scott Mattila and Art Gross emphasize the importance of involving multiple stakeholders in the risk assessment process to capture all relevant risks. Mattila advises that a team comprising clinical, administrative, and IT staff should conduct checks frequently to gain a complete risk view. Meanwhile, Gross suggests that risk assessments should be integrated into yearly business reviews. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of security awareness and ensures that all potential vulnerabilities are addressed. Furthermore, entities should employ automated tools for data discovery and threat detection, simplifying the identification of ePHI vulnerabilities and enhancing overall adherence efforts.
Incorporating lessons learned from case studies, such as the breaches experienced by LA Care Health Plan and Banner Health, illustrates the consequences of inadequate risk management. These incidents serve as a stark reminder that failing to conduct comprehensive risk analyses can lead to severe financial penalties, ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum of $1.5 million per year for repeated issues, alongside damage to patient trust. Therefore, emphasizing risk assessment is not merely a regulatory requirement; it is a strategic necessity for healthcare organizations committed to safeguarding patient information in accordance with HIPAA and upholding industry standards.
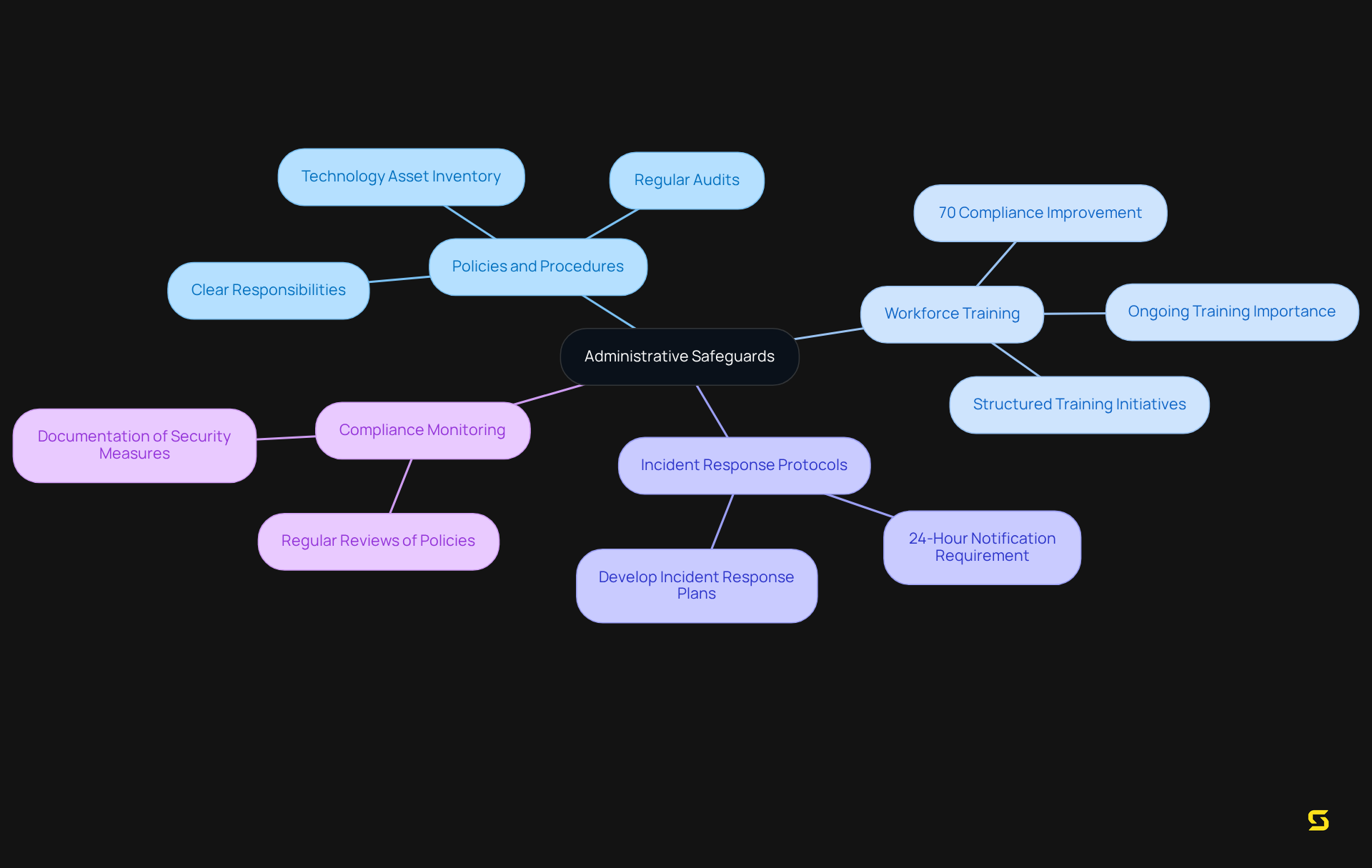
Implement Administrative Safeguards
Administrative safeguards encompass a comprehensive set of policies and procedures that govern the selection, development, implementation, and maintenance of essential protective measures for regulatory compliance. A dedicated security officer must be appointed, comprehensive workforce training conducted, and robust incident response protocols established. Research indicates that organizations with structured training initiatives see a significant enhancement in adherence effectiveness, with data showing that well-trained personnel are 70% more likely to comply with .
Compliance officers stress the importance of ongoing training, asserting that 'a well-informed workforce is the first line of defense against data breaches' (Joey O'Bryhim, NACCHO Staff). By establishing these safeguards, organizations cultivate a culture of accountability and awareness among employees, ensuring that everyone comprehends their role in safeguarding electronic protected health information (ePHI).
Effective administrative protections necessitate the formulation of clear policies delineating responsibilities, conducting regular training sessions to keep staff informed about compliance requirements, and developing incident response plans that outline the necessary actions in the event of a data breach. For SaaS companies, implementing effective policies may involve:
- Regular audits of security practices
- Integration of technological solutions that bolster data protection
Moreover, it is imperative for business partners to notify covered entities within 24 hours of executing their contingency plans, as mandated by the new privacy regulations. By prioritizing these administrative protections, organizations can significantly fortify their HIPAA compliance posture and mitigate risks associated with ePHI management.
Additionally, the proposed amendments to the Security Rule will abolish the distinction between 'required' and 'addressable' implementation specifications, making all measures mandatory. Regulated organizations must adhere to nine standards for administrative safeguards that protect ePHI, underscoring the critical nature of these measures.
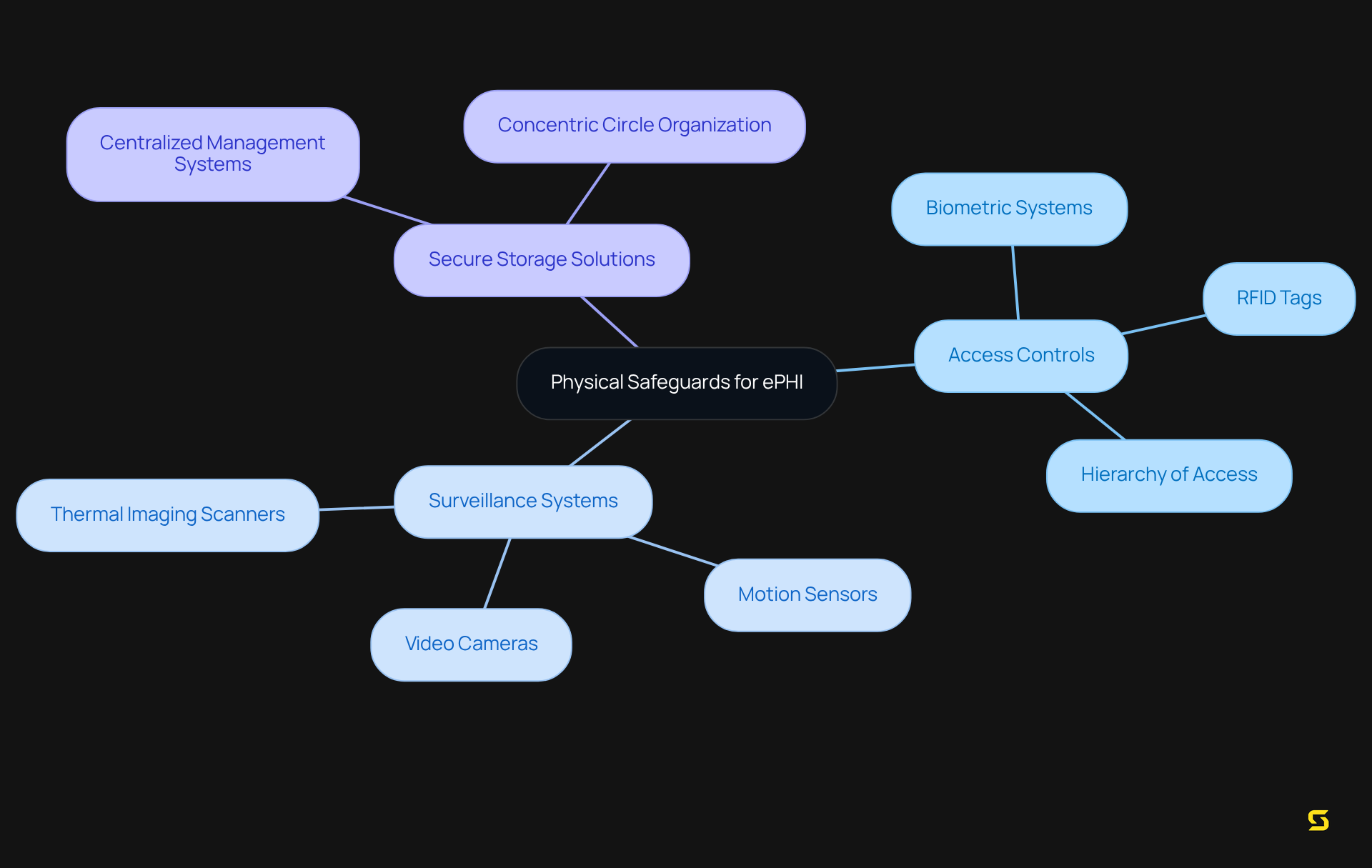
Establish Physical Safeguards
Establishing robust physical safeguards is imperative for the protection of electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) within healthcare facilities. This encompasses a comprehensive suite of security measures, including:
- Access controls
- Surveillance systems
- Secure storage solutions
Access control systems are vital; they guarantee that only authorized personnel can access sensitive areas, significantly mitigating the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with HIPAA. Healthcare institutions are increasingly investing in advanced access control technologies, such as biometric systems and RFID tags, to effectively monitor and manage access.
Recent trends indicate a growing reliance on hybrid-cloud frameworks, with 68% of healthcare entities planning to migrate more of their physical data to the cloud in the next 18 months. This transition not only enhances scalability but also ensures that we meet HIPAA compliance requirements. , including video cameras and motion sensors, are essential for monitoring critical areas, ensuring that any unauthorized access is swiftly detected and addressed. Alarmingly, 46% of organizations reported an increase in employee injuries due to incidents, underscoring the urgent need for strong physical protection measures.
Moreover, integrating physical protection measures into a centralized management system fosters seamless communication between devices, thereby enhancing overall safety. For example, organizing monitoring systems in concentric circles allows for efficient oversight and rapid response to incidents, facilitating communication among surveillance cameras, motion sensors, and other protective devices. Industry experts stress that maintaining a hierarchy of access tailored to the needs of patients and employees is crucial for safeguarding ePHI. Mark Feider from Genetec points out that the healthcare sector is progressively adopting hybrid and cloud security deployments to achieve a balance of control, cost, and flexibility.
In conclusion, the implementation of comprehensive physical safeguards, including advanced access control measures and surveillance technologies, is essential for healthcare organizations to protect sensitive information and comply with privacy regulations.
Utilize Technical Safeguards
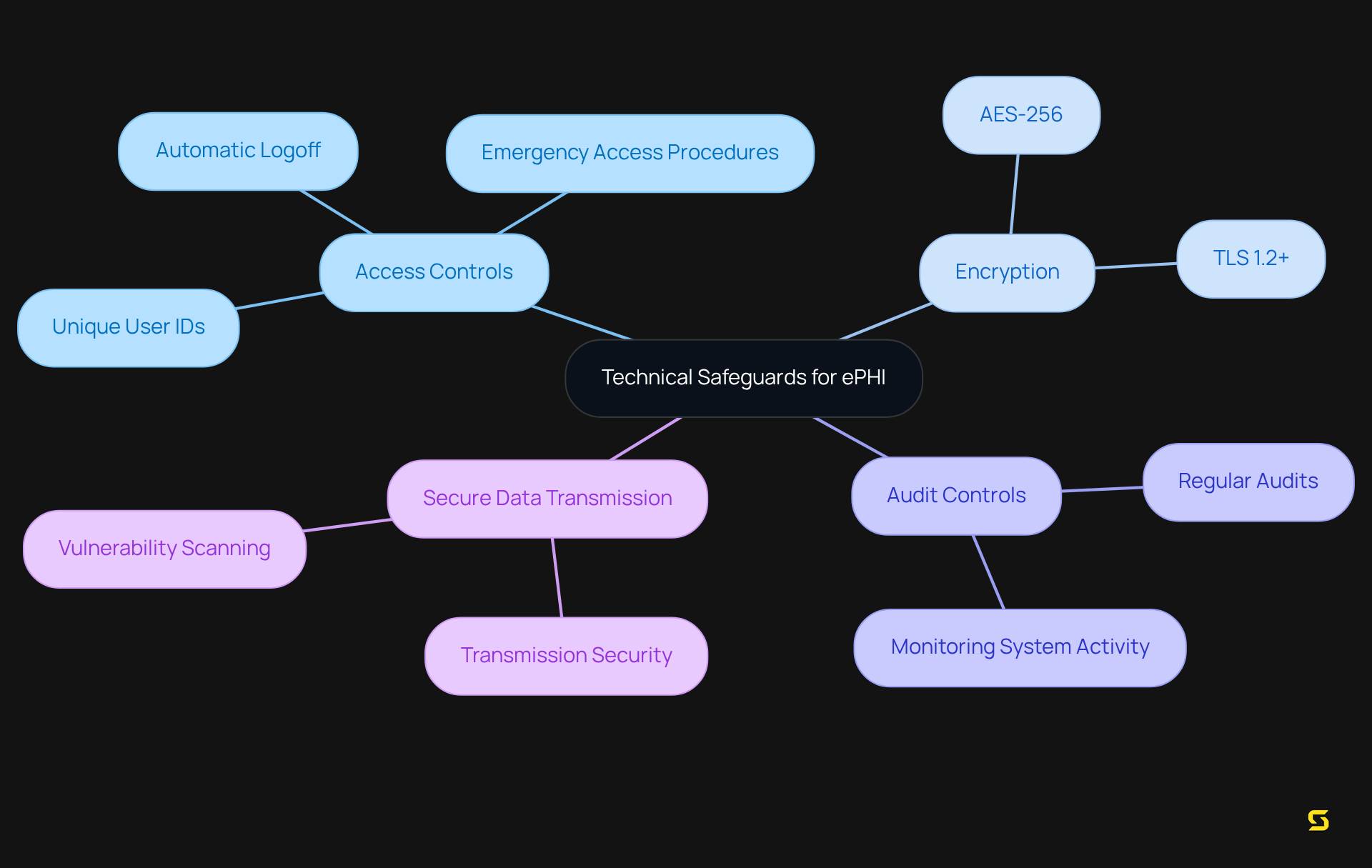
Technical safeguards are essential for the protection of electronic protected health information (ePHI). These safeguards encompass:
- Access controls
- Encryption
- Audit controls
- Secure data transmission methods
Organizations must implement robust technical measures to guarantee that ePHI is accessible solely to authorized users, ensuring data integrity throughout its lifecycle. Notably, a significant portion of organizations—over 70%—are now utilizing encryption technologies to secure ePHI. This trend underscores an increasing awareness of the critical importance of .
Cybersecurity experts assert that encryption not only safeguards sensitive data but also fosters trust with patients and partners, demonstrating a commitment to responsible data management. For example, adopting encryption standards such as AES-256 for data at rest and TLS 1.2+ for data in transit is crucial for compliance.
Furthermore, regular audits and monitoring of these systems are imperative to adapt to evolving security threats, ensuring that organizations remain vigilant against potential breaches. By integrating these technical safeguards, healthcare software can effectively protect ePHI while fulfilling HIPAA regulatory requirements.
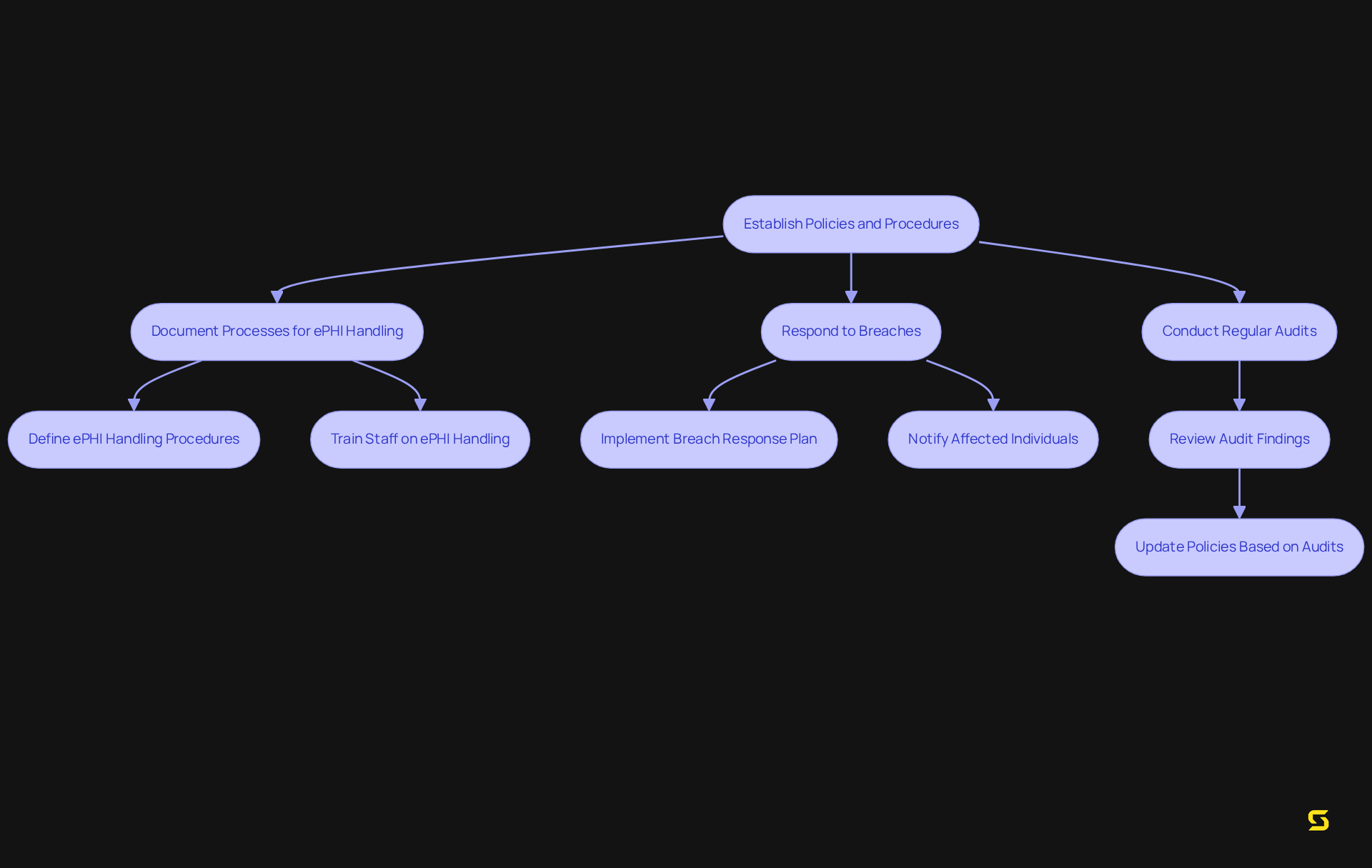
Create Policies and Procedures
Organizations must establish comprehensive policies and procedures that clearly outline their commitment to adhering to HIPAA regulations regarding health information. This entails documenting precise processes for handling electronic (ePHI) in accordance with HIPAA, responding effectively to breaches, and conducting regular audits. Such transparent policies not only ensure that all staff understand their responsibilities but also underscore the critical importance of safeguarding patient information. By fostering a culture of adherence, organizations can significantly enhance their compliance efforts.
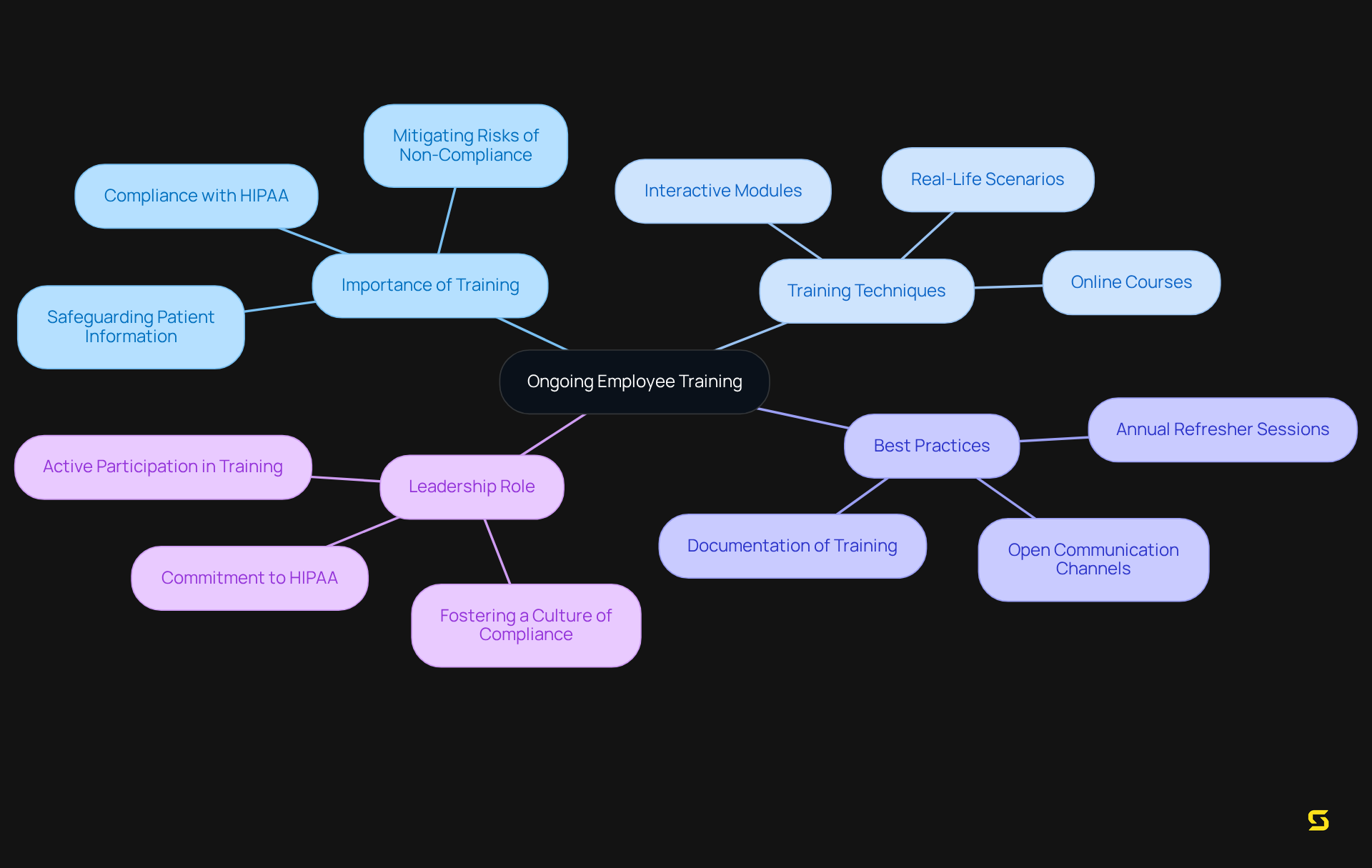
Provide Ongoing Employee Training
Continuous employee education is vital for ensuring adherence to HIPAA regulations, as well as organizational policies and security best practices. Effective training programs must be tailored to address the specific needs of various roles within the organization, including front-office staff, healthcare providers, and IT professionals. Regular updates to training materials are essential to reflect changes in regulations and technology, ensuring that employees remain informed and equipped to navigate regulatory challenges.
Investing in comprehensive training empowers staff to proactively identify and address potential compliance issues. Organizations that implement engaging training techniques—such as interactive modules, real-life scenarios, and regular refresher courses—experience higher retention rates and improved understanding of regulatory requirements.
Best practices for privacy training encompass:
- Conducting annual refresher sessions
- Utilizing online courses for flexibility
- Encouraging open communication channels after training to resolve any uncertainties
Leadership involvement in HIPAA training is crucial for fostering a culture of compliance, as employees are more likely to value adherence when they see leadership's commitment to HIPAA. Customizing training to specific roles enhances its effectiveness, making it more relevant and impactful for employees. Moreover, maintaining records of training sessions is critical for legal compliance and accountability. This commitment to ongoing education not only safeguards patient information but also fortifies a culture of compliance within the organization. Non-compliance with health privacy regulations can result in substantial fines and reputational damage, highlighting the necessity of effective training. To implement continuous training successfully, organizations should consider to ensure comprehensive coverage of regulatory requirements.
Perform Regular Audits and Assessments
Routine evaluations and reviews are essential for entities to assess their compliance with health regulations, particularly HIPAA, and identify areas needing improvement. Data indicate that approximately 30% of entities conduct annual health information privacy audits, underscoring the importance of this practice. These audits must include to ensure their effectiveness and relevance in compliance with HIPAA.
For instance, the upcoming 2024-2025 audits under the health information privacy regulations will assess 50 covered entities and business partners, focusing on compliance with critical Security Rule requirements to combat cyber threats such as hacking and ransomware. By consistently evaluating compliance with HIPAA, entities not only mitigate risks but also demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding patient information.
As industry expert Steve Smith asserts, "HHS must regularly audit organizations for regulatory adherence," highlighting the critical nature of these evaluations. Adopting a structured approach to these audits, as detailed in the OCR's comprehensive audit protocol, can significantly enhance an organization's capacity to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI) and uphold trust with patients and stakeholders.
Furthermore, a report from HHS’ Office of Inspector General (OIG) in November 2024 revealed that the previous audit program was ineffective in improving cybersecurity, emphasizing the urgent need for thorough compliance assessments.
Stay Updated on HIPAA Regulations
Organizations must actively monitor updates to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations and adjust their adherence strategies accordingly. This requires:
- Subscribing to industry newsletters
- Attending training sessions
- Participating in professional groups
Healthcare practitioners who have established organized adherence programs demonstrate a stronger capacity to respond to audits and breach investigations, underscoring the effectiveness of proactive strategies. Statistics reveal that entities engaged in regular training and updates are significantly better equipped to , showing a notable increase in adherence to new regulations.
Compliance experts assert that continuous education on HIPAA updates is essential for compliance officers and IT teams, as it fosters a culture of awareness and preparedness regarding HIPAA. By staying informed about regulatory changes, organizations can ensure their policies and procedures effectively protect electronic protected health information (ePHI) and mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
Conclusion
Ensuring HIPAA compliance in Software as a Service (SaaS) products is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a crucial component for the protection of patient data and the trust of healthcare providers. By adopting a comprehensive strategy that includes:
- A thorough understanding of the HIPAA Security Rule
- Conducting detailed risk analyses
- Implementing robust administrative, physical, and technical safeguards
organizations can effectively navigate the complexities of compliance. This commitment not only meets regulatory standards but also enhances the overall security posture of healthcare entities.
Key insights from the article underscore the importance of ongoing employee training, the establishment of clear policies and procedures, and the necessity of regular audits to maintain compliance. Each of these elements plays a vital role in fostering a culture of security awareness and accountability, ensuring that organizations are well-equipped to handle the evolving landscape of healthcare regulations. Furthermore, staying updated on HIPAA regulations through continuous education and proactive engagement with industry developments is essential for long-term success.
In a landscape where data breaches and regulatory penalties can have devastating consequences, the significance of HIPAA compliance cannot be overstated. By prioritizing these essential steps, organizations not only safeguard sensitive health information but also build trust with patients and partners, ultimately contributing to a more secure and reliable healthcare ecosystem. Taking action now to enhance compliance efforts will not only protect patient data but also position organizations as leaders in the healthcare technology sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is SDA and its role in software development for healthcare?
SDA specializes in custom software development that complies with health regulations such as HIPAA, enabling healthcare organizations to securely manage protected health information (PHI) while enhancing user experience.
What percentage of healthcare organizations have achieved HIPAA compliance as of March 2024?
As of March 5, 2024, 92% of healthcare organizations have achieved regulatory compliance with HIPAA.
What are some key security measures implemented by SDA?
Key security measures implemented by SDA include encryption, access controls, and regular audits concerning the storage and transmission of PHI.
What is the HIPAA Security Rule?
The HIPAA Security Rule establishes national standards for protecting electronic protected health information (ePHI) and requires covered entities to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
What are the main components of the HIPAA Security Rule?
The main components include conducting comprehensive risk assessments, maintaining records of technology assets, implementing multi-factor authentication and encryption, and performing regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
Why is risk assessment important for healthcare organizations?
Risk assessment is crucial for protecting ePHI, ensuring regulatory compliance, and identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and weaknesses in data management practices.
What was the impact of large-scale breaches reported in 2023?
In 2023, there were 553 large-scale breaches affecting over 109 million patients, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive risk assessments in healthcare organizations.
How can organizations enhance their risk assessment processes?
Organizations can enhance their risk assessment processes by involving multiple stakeholders, integrating assessments into yearly business reviews, and utilizing automated tools for data discovery and threat detection.
What are the financial consequences of failing to comply with HIPAA regulations?
Non-compliance with HIPAA regulations can lead to financial penalties ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum of $1.5 million per year for repeated violations, as well as damage to patient trust.
What is the projected cost for regulated organizations to comply with HIPAA regulations?
The projected first-year expenses for regulated organizations and health plan sponsors to adhere to HIPAA regulations are around $9.3 billion.





